KinD
- Description: osmo-sensing two-component sensor kinase, phosphorylates Spo0F, part of the phosphorelay, checkpoint protein that links sporulation initiation to biofilm formation
| Gene name | kinD |
| Synonyms | ykvD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | initiation of sporulation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: kinD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: KinD | |
| Function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay | |
| MW, pI | 56 kDa, 6.745 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1518 bp, 506 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | eag, mhqR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 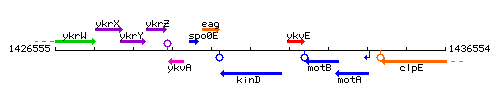
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed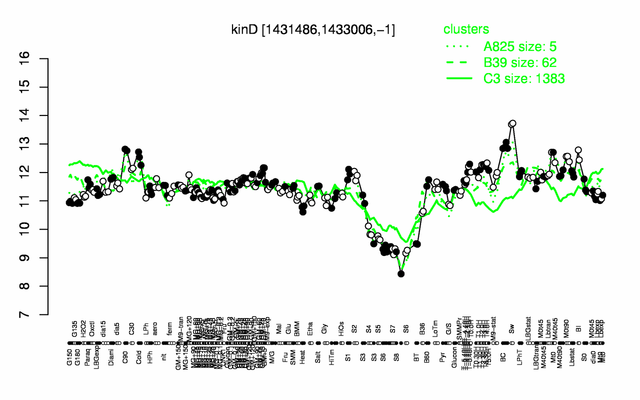
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein modification, transcription factors and their control, phosphorelay, biofilm formation, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13660
Phenotypes of a mutant
- deletion of kinD suppresses the sporulation defect of matrix mutants, while its overproduction delays sporulation PubMed
- inactivation of kinD restores beta-lactam resistance in a sigM mutant PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of Spo0F, regulates the onset of sporulation by inhibiting the activity of Spo0A until matrix, or a component therein, is sensed PubMed
- dual role as a phosphatase or a kinase, activity is linked to the presence of extracellular matrix in the biofilms PubMed
- mainly active in the younger, outer regions of a colony (with KinC) PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- activity is stimulated by direct or indirect interaction with Med PubMed
- L-malate seems to trigger KinD activity PubMed, but this effect may be indirect due to the excretion of pyruvate that directly binds the extracytoplasmic sensing domain of KinD PubMed
- kinase activity is triggered and phosphatase activity is decreased by increased osmotic pressure PubMed
- activity is triggered in the presence of glycerol + manganese PubMed
- Localization: membrane
Database entries
- UniProt: O31671
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Moshe Shemesh, Yunrong Chai
A combination of glycerol and manganese promotes biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis via histidine kinase KinD signaling.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(12);2747-54
[PubMed:23564171]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
R Wu, M Gu, R Wilton, G Babnigg, Y Kim, P R Pokkuluri, H Szurmant, A Joachimiak, M Schiffer
Insight into the sporulation phosphorelay: crystal structure of the sensor domain of Bacillus subtilis histidine kinase, KinD.
Protein Sci: 2013, 22(5);564-76
[PubMed:23436677]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shmuel M Rubinstein, Ilana Kolodkin-Gal, Anna McLoon, Liraz Chai, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick, David A Weitz
Osmotic pressure can regulate matrix gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 86(2);426-36
[PubMed:22882172]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yun Chen, Shugeng Cao, Yunrong Chai, Jon Clardy, Roberto Kolter, Jian-hua Guo, Richard Losick
A Bacillus subtilis sensor kinase involved in triggering biofilm formation on the roots of tomato plants.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 85(3);418-30
[PubMed:22716461]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yun Luo, John D Helmann
Analysis of the role of Bacillus subtilis σ(M) in β-lactam resistance reveals an essential role for c-di-AMP in peptidoglycan homeostasis.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 83(3);623-39
[PubMed:22211522]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Elizabeth A Shank, Vanja Klepac-Ceraj, Leonardo Collado-Torres, Gordon E Powers, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
Interspecies interactions that result in Bacillus subtilis forming biofilms are mediated mainly by members of its own genus.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2011, 108(48);E1236-43
[PubMed:22074846]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Allison V Banse, Errett C Hobbs, Richard Losick
Phosphorylation of Spo0A by the histidine kinase KinD requires the lipoprotein med in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(15);3949-55
[PubMed:21622736]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Anna L McLoon, Ilana Kolodkin-Gal, Shmuel M Rubinstein, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Spatial regulation of histidine kinases governing biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(3);679-85
[PubMed:21097618]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Claudio Aguilar, Hera Vlamakis, Alejandra Guzman, Richard Losick, Roberto Kolter
KinD is a checkpoint protein linking spore formation to extracellular-matrix production in Bacillus subtilis biofilms.
mBio: 2010, 1(1);
[PubMed:20689749]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
M Jiang, W Shao, M Perego, J A Hoch
Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 38(3);535-42
[PubMed:11069677]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)