GerD
- Description: required for clustering of germinant receptors in the spore inner membrane
| Gene name | gerD |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | lipoprotein |
| Function | germination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gerD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GerD | |
| MW, pI | 20 kDa, 4.862 |
| Gene length, protein length | 555 bp, 185 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | salA, kbaA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 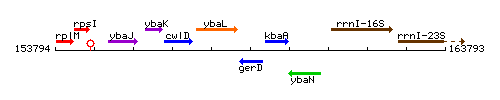
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed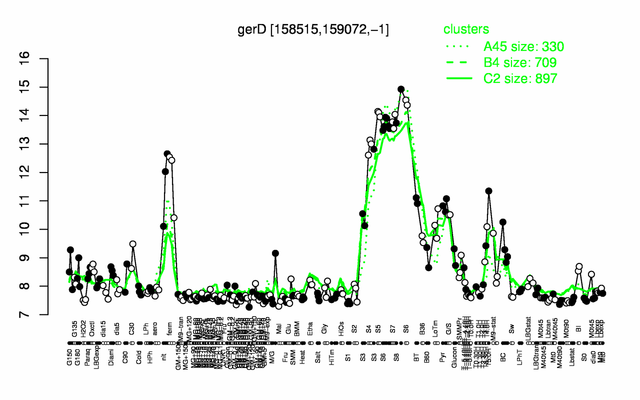
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
germination, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01550
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: required for clustering of germinant receptors in the spore inner membrane PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P16450
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- expression level depends on sporulation conditions (medim composition, temperature) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in Anne Moir lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Anne Moir, University of Sheffield, UK
Your additional remarks
References
Additional references: PubMed
Kerry-Ann V Stewart, Xuan Yi, Sonali Ghosh, Peter Setlow
Germination protein levels and rates of germination of spores of Bacillus subtilis with overexpressed or deleted genes encoding germination proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(12);3156-64
[PubMed:22493018]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Arturo Ramirez-Peralta, Pengfei Zhang, Yong-Qing Li, Peter Setlow
Effects of sporulation conditions on the germination and germination protein levels of Bacillus subtilis spores.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2012, 78(8);2689-97
[PubMed:22327596]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Xuan Yi, Jintao Liu, James R Faeder, Peter Setlow
Synergism between different germinant receptors in the germination of Bacillus subtilis spores.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(18);4664-71
[PubMed:21725007]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Keren K Griffiths, Jingqiao Zhang, Ann E Cowan, Ji Yu, Peter Setlow
Germination proteins in the inner membrane of dormant Bacillus subtilis spores colocalize in a discrete cluster.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(4);1061-77
[PubMed:21696470]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wiyada Mongkolthanaruk, Carl Robinson, Anne Moir
Localization of the GerD spore germination protein in the Bacillus subtilis spore.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 4);1146-1151
[PubMed:19332816]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patricia L Pelczar, Peter Setlow
Localization of the germination protein GerD to the inner membrane in Bacillus subtilis spores.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(16);5635-41
[PubMed:18556788]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patricia L Pelczar, Takao Igarashi, Barbara Setlow, Peter Setlow
Role of GerD in germination of Bacillus subtilis spores.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(3);1090-8
[PubMed:17122337]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E H Kemp, R L Sammons, A Moir, D Sun, P Setlow
Analysis of transcriptional control of the gerD spore germination gene of Bacillus subtilis 168.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(15);4646-52
[PubMed:1906867]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J R Yon, R L Sammons, D A Smith
Cloning and sequencing of the gerD gene of Bacillus subtilis.
J Gen Microbiol: 1989, 135(12);3431-45
[PubMed:2517635]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)