TagA
- Description: UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine transferase
| Gene name | tagA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed, no PubMed |
| Product | UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine transferase |
| Function | biosynthesis of teichoic acid |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: tagA | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 10.133 |
| Gene length, protein length | 768 bp, 256 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | tagD, tagB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 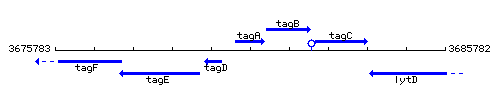
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed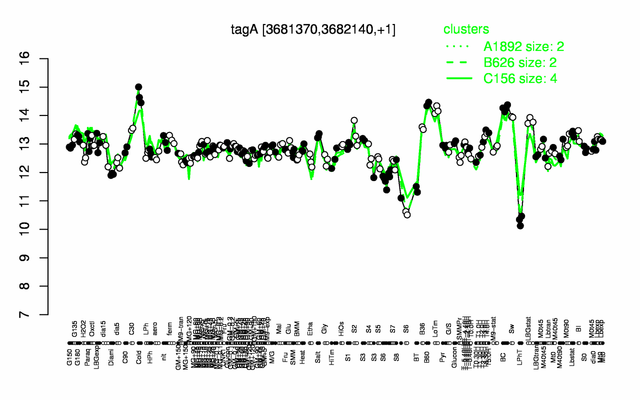
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35750
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed, reduced growth rate, loss of rod-like morphology PubMed
- inactivation of tagA strongly restores beta-lactam resistance in a sigM mutant PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine + N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyldiphosphoundecaprenol = UDP + N-acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminyl-1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyldiphosphoundecaprenol (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: glycosyltransferase 26 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- secreted (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P27620
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.4.1.187
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Michael A D'Elia, James A Henderson, Terry J Beveridge, David E Heinrichs, Eric D Brown
The N-acetylmannosamine transferase catalyzes the first committed step of teichoic acid assembly in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(12);4030-4
[PubMed:19376878]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alex Formstone, Rut Carballido-López, Philippe Noirot, Jeffery Errington, Dirk-Jan Scheffers
Localization and interactions of teichoic acid synthetic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(5);1812-21
[PubMed:18156271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alistair Howell, Sarah Dubrac, Kasper Krogh Andersen, David Noone, Juliette Fert, Tarek Msadek, Kevin Devine
Genes controlled by the essential YycG/YycF two-component system of Bacillus subtilis revealed through a novel hybrid regulator approach.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(6);1639-55
[PubMed:12950927]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Qi, F M Hulett
Role of Pho-P in transcriptional regulation of genes involved in cell wall anionic polymer biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(15);4007-10
[PubMed:9683503]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Liu, S Eder, F M Hulett
Analysis of Bacillus subtilis tagAB and tagDEF expression during phosphate starvation identifies a repressor role for PhoP-P.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(3);753-8
[PubMed:9457886]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Mauël, A Bauduret, C Chervet, S Beggah, D Karamata
In Bacillus subtilis 168, teichoic acid of the cross-wall may be different from that of the cylinder: a hypothesis based on transcription analysis of tag genes.
Microbiology (Reading): 1995, 141 ( Pt 10);2379-89
[PubMed:7581998]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Mauël, M Young, A Monsutti-Grecescu, S A Marriott, D Karamata
Analysis of Bacillus subtilis tag gene expression using transcriptional fusions.
Microbiology (Reading): 1994, 140 ( Pt 9);2279-88
[PubMed:7952180]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)