IlvB
- Description: acetolactate synthase (large subunit)
| Gene name | ilvB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetolactate synthase (large subunit) |
| Function | biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ile, Leu, Val, Coenzyme A | |
| MW, pI | 62 kDa, 5.178 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1722 bp, 574 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ilvH, ysnD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 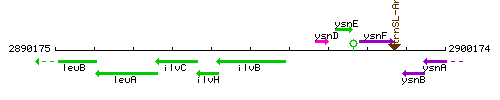
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, CcpA regulon, TnrA regulon, T-box
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO2 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: TPP enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 1N53 (T box RNA)
- UniProt: P37251
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.2.1.6
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: for a complete overview on the regulation of the ilv operon, see Brinsmade et al.
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP324, ilvB under control of pXyl (cat), available in Jörg Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion: pGP520 and pGP524 (both in pAC5), available in Stülke lab; pGP523 (in pAC6), available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Shaun R Brinsmade, Roelco J Kleijn, Uwe Sauer, Abraham L Sonenshein
Regulation of CodY activity through modulation of intracellular branched-chain amino acid pools.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(24);6357-68
[PubMed:20935095]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ana Gutiérrez-Preciado, Tina M Henkin, Frank J Grundy, Charles Yanofsky, Enrique Merino
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(1);36-61
[PubMed:19258532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Molecular mechanisms underlying the positive stringent response of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon, involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(18);6134-47
[PubMed:18641142]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of CodY-binding sites in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(4);1224-36
[PubMed:18083814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frank Wiegeshoff, Mohamed A Marahiel
Characterization of a mutation in the acetolactate synthase of Bacillus subtilis that causes a cold-sensitive phenotype.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2007, 272(1);30-4
[PubMed:17488331]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kaori Morisaki, Josef Deutscher, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Elaborate transcription regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through global regulators of CcpA, CodY and TnrA.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 56(6);1560-73
[PubMed:15916606]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Robert P Shivers, Abraham L Sonenshein
Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 56(6);1549-59
[PubMed:15916605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kaori Morisaki, Ken-Ichi Yoshida, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Negative transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon for biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through the Bacillus subtilis global regulator TnrA.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(23);7971-9
[PubMed:15547269]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Susanne Hennig, Michael Hecker, Georg Homuth
Transcriptional organization and posttranscriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(8);2240-52
[PubMed:15060025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Ludwig, Christoph Meinken, Anastasija Matin, Jörg Stülke
Insufficient expression of the ilv-leu operon encoding enzymes of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis limits growth of a Bacillus subtilis ccpA mutant.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(18);5174-8
[PubMed:12193635]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
Conservation of a transcription antitermination mechanism in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and amino acid biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria.
J Mol Biol: 1994, 235(2);798-804
[PubMed:8289305]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Grandoni, S A Zahler, J M Calvo
Transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(10);3212-9
[PubMed:1577690]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)