Sda
- Description: developmental checkpoint protein, inhibits the autokinase activity of KinA and KinB, control of the phosphorelay
| Gene name | sda |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | developmental checkpoint protein |
| Function | mediates a developmental checkpoint coupling initiation of sporulation (phosphorylation of Spo0A) to the function of replication initiation proteins |
| Function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay | |
| MW, pI | 6 kDa, 5.605 |
| Gene length, protein length | 156 bp, 52 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yloV, yqeF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 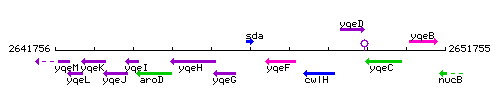
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU25690
Phenotypes of a mutant
- sporulates at a higher frequency
- will sporulate in the presence of replication stress
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
Categories containing this gene/protein
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Sda is a checkpoint protein that is upregulated in response to replication stress PubMed. Sda inhibits the autokinase activity of KinA (and likely KinB as well). This in its turn results in reduced levels of Spo0A~P. Thus, replication stressed cells will not initiate sporulation.
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: Q7WY62
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Sda is rapidly turned over by the ClpP/X system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus PubMed.
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: Sda is rapidly turned over by the ClpP/X system because of some uncharged residues at its C-terminus PubMed.
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Jan-Willem Veening, Heath Murray, Jeff Errington
A mechanism for cell cycle regulation of sporulation initiation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 2009, 23(16);1959-70
[PubMed:19684115]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David A Jacques, Margaret Streamer, Susan L Rowland, Glenn F King, J Mitchell Guss, Jill Trewhella, David B Langley
Structure of the sporulation histidine kinase inhibitor Sda from Bacillus subtilis and insights into its solution state.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr: 2009, 65(Pt 6);574-81
[PubMed:19465772]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew J Bick, Valerie Lamour, Kanagalaghatta R Rajashankar, Yuliya Gordiyenko, Carol V Robinson, Seth A Darst
How to switch off a histidine kinase: crystal structure of Geobacillus stearothermophilus KinB with the inhibitor Sda.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 386(1);163-77
[PubMed:19101565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shu Ishikawa, Yoshitoshi Ogura, Mika Yoshimura, Hajime Okumura, Eunha Cho, Yoshikazu Kawai, Ken Kurokawa, Taku Oshima, Naotake Ogasawara
Distribution of stable DnaA-binding sites on the Bacillus subtilis genome detected using a modified ChIP-chip method.
DNA Res: 2007, 14(4);155-68
[PubMed:17932079]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Andrew E Whitten, David A Jacques, Boualem Hammouda, Tracey Hanley, Glenn F King, J Mitchell Guss, Jill Trewhella, David B Langley
The structure of the KinA-Sda complex suggests an allosteric mechanism of histidine kinase inhibition.
J Mol Biol: 2007, 368(2);407-20
[PubMed:17350039]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michael V Ruvolo, Kathleen E Mach, William F Burkholder
Proteolysis of the replication checkpoint protein Sda is necessary for the efficient initiation of sporulation after transient replication stress in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 60(6);1490-508
[PubMed:16796683]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Nora Au, Elke Kuester-Schoeck, Veena Mandava, Laura E Bothwell, Susan P Canny, Karen Chachu, Sierra A Colavito, Shakierah N Fuller, Eli S Groban, Laura A Hensley, Theresa C O'Brien, Amish Shah, Jessica T Tierney, Louise L Tomm, Thomas M O'Gara, Alexi I Goranov, Alan D Grossman, Charles M Lovett
Genetic composition of the Bacillus subtilis SOS system.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(22);7655-66
[PubMed:16267290]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Susan L Rowland, William F Burkholder, Katherine A Cunningham, Mark W Maciejewski, Alan D Grossman, Glenn F King
Structure and mechanism of action of Sda, an inhibitor of the histidine kinases that regulate initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2004, 13(5);689-701
[PubMed:15023339]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W F Burkholder, I Kurtser, A D Grossman
Replication initiation proteins regulate a developmental checkpoint in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2001, 104(2);269-79
[PubMed:11207367]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)