PonA
- Description: class A penicillin-binding protein 1A/1B, contributes to cell elongation and cell division
| Gene name | ponA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | penicillin-binding protein 1A/1B |
| Function | bifunctional glucosyltransferase/ transpeptidase |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ponA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PonA | |
| MW, pI | 99 kDa, 4.752 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2742 bp, 914 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | recU, ypoC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 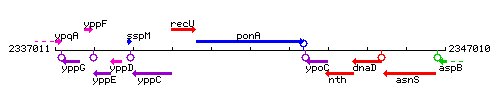
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed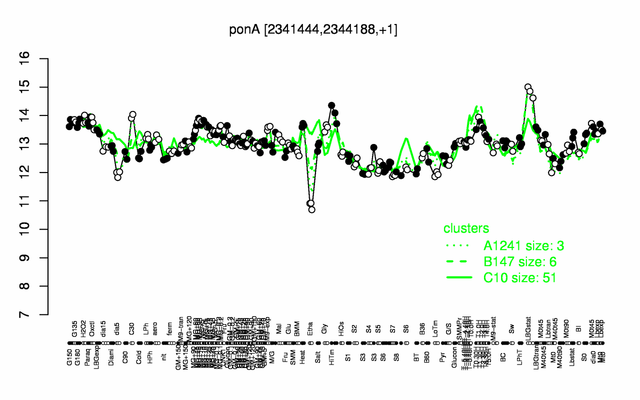
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22320
Phenotypes of a mutant
- prevents bulging of the cells when grown at low Mg(2+) concentrations, suppresses the lethal effect of a mreB mutation PubMed
- deletion of ponA restores growth and normal shape of a yvcK mutant on gluconeogenic carbon sources PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39793
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: constitutive during vegetative growth PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jeff Errington lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Elitza I Tocheva, Javier López-Garrido, H Velocity Hughes, Jennifer Fredlund, Erkin Kuru, Michael S Vannieuwenhze, Yves V Brun, Kit Pogliano, Grant J Jensen
Peptidoglycan transformations during Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(4);673-86
[PubMed:23531131]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Elodie Foulquier, Frédérique Pompeo, Alain Bernadac, Leon Espinosa, Anne Galinier
The YvcK protein is required for morphogenesis via localization of PBP1 under gluconeogenic growth conditions in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 80(2);309-18
[PubMed:21320184]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Richard A Daniel, Jeffery Errington
Regulation of cell wall morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis by recruitment of PBP1 to the MreB helix.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 71(5);1131-44
[PubMed:19192185]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dennis Claessen, Robyn Emmins, Leendert W Hamoen, Richard A Daniel, Jeff Errington, David H Edwards
Control of the cell elongation-division cycle by shuttling of PBP1 protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 68(4);1029-46
[PubMed:18363795]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Warawan Eiamphungporn, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);830-48
[PubMed:18179421]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Dirk-Jan Scheffers, Jeffery Errington
PBP1 is a component of the Bacillus subtilis cell division machinery.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(15);5153-6
[PubMed:15262952]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Dirk-Jan Scheffers, Laura J F Jones, Jeffery Errington
Several distinct localization patterns for penicillin-binding proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(3);749-64
[PubMed:14731276]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L B Pedersen, E R Angert, P Setlow
Septal localization of penicillin-binding protein 1 in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(10);3201-11
[PubMed:10322023]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Murray, D L Popham, P Setlow
Bacillus subtilis cells lacking penicillin-binding protein 1 require increased levels of divalent cations for growth.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(17);4555-63
[PubMed:9721295]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D L Popham, P Setlow
Phenotypes of Bacillus subtilis mutants lacking multiple class A high-molecular-weight penicillin-binding proteins.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(7);2079-85
[PubMed:8606187]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D L Popham, P Setlow
Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and mutagenesis of the Bacillus subtilis ponA operon, which codes for penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 1 and a PBP-related factor.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(2);326-35
[PubMed:7814321]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)