Rny
- Description: RNase Y, 5' end sensitive endoribonuclease, involved in the degradation/ processing of mRNA
| Gene name | rny |
| Synonyms | ymdA |
| Essential | no PubMed |
| Product | RNase Y |
| Function | RNA processing and degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rny | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Rny | |
| Regulatory function of this protein in SubtiPathways: rny | |
| MW, pI | 58,7 kDa, 5.39 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1560 bp, 520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | pbpX, ymdB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 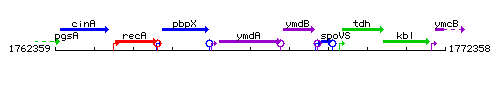
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed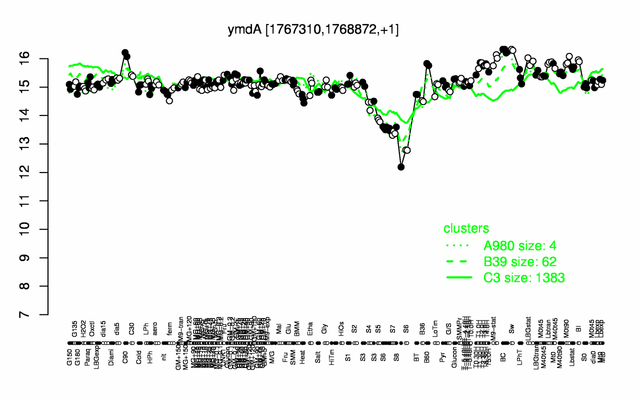
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
Rnases, biofilm formation, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Targets of RNase Y
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16960
Phenotypes of a mutant
- transcription profile resulting from rny depletion: GEO PubMed
- defect in spore germination PubMed
- a study from the lab of Ciaran Condon reports that rny is non-essential and that the mutant is strongly impaired in sporulation, genetic competence and many other phenotypes PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- RNase Y cleaves S-box riboswitch RNAs in vivo and in vitro PubMed
- preference for 5' monophosphorylated substrate in vitro PubMed
- endonucleolytic cleavage PubMed
- required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA PubMed
- cleavage activity appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure PubMed
- RNase Y initiates the degradation of rpsO mRNA PubMed
- RNase Y is responsible for the degradation of 23S rRNA, 16S rRNA, and mRNAs in aging spores PubMed
- RNase Y cleaves the leader of the cwlO mRNA at a stem-loop structure PubMed
- Protein family: Member of the HD superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases; 2',3' cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): requires Mg+2, which can be replaced by Zn+2 or Mn+2 ions, PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity: appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure, PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31774
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.1.4.16
Additional information
required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: constitutive
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- 4043 (rny under p-spac control, cat), GP193 (rny under p-xyl control, cat), both available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- SSB447 (rny under P-spac control, "erm") available in Putzer lab.
- Expression vector:
- N-terminal Strep-tag, expression in E. coli, in pGP172: pGP441, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP380: pGP775, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- C-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP382: pGP1852, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression of RNase Y missing the N-terminal transmembrane domain (25aa) as an intein fusion in E. coli (no tag left in the purified protein) available in the Putzer lab
- wild type rny, expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1201, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- there is also a series of domain constructs present in pBQ200, all available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- chromosomal expression of Rny-Strep, spc: GP1033, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP459 (in pAC7), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- B. subtilis 3569 (amyE:: (p-xyl rny-gfpmut1-spc)), available in Errington lab
- pGP1368 for chromosomal expression of rny-YFP, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct: GP1030 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in van Dijl and in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Ciaran Condon, IBPC Paris, France Homepage
- Harald Putzer, IBPC Paris, France Homepage
- Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Publications on B. subtilis rny
Publications on homologs from other organisms