LytE
- Description: cell wall hydrolase (major autolysin) for cell elongation and separation, D,L-endopeptidase-type autolysin
| Gene name | lytE |
| Synonyms | papQ, cwlF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | cell wall hydrolase (major autolysin),endopeptidase-type autolysin |
| Function | major autolysin, cell elongation and separation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: lytE | |
| MW, pI | 37 kDa, 10.713 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1029 bp, 343 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | phoA, citR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 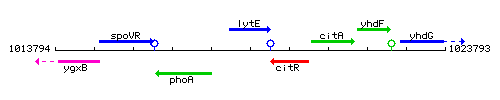
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed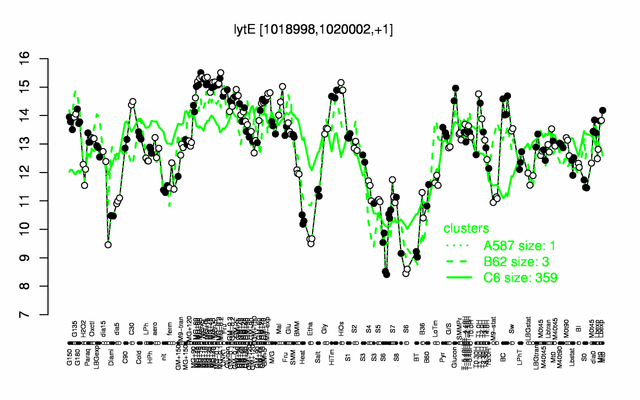
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall degradation/ turnover, cell wall synthesis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigH regulon, SigI regulon, Spo0A regulon, WalR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU09420
Phenotypes of a mutant
- a cwlO lytE mutant is not viable PubMed
- growth defect at high temperature PubMed
- inactivation of lytE strongly restores beta-lactam resistance in a sigM mutant by delaying cell lysis PubMed
- a lytE mutation is synthetically lethal with ftsE and ftsX mutation (due to a lack of autolysin activity) PubMed
- a lytE mutation increases the cell separation defect of a lytF mutant PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: nlpC/p60 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): the C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domains of LytE, LytF, CwlS, and CwlO exhibit strong sequence similarity
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domain PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54421
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: lytE PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications