AmyE
- Description: alpha-amylase
| Gene name | amyE |
| Synonyms | amyA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | alpha-amylase) |
| Function | starch degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: amyE | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 72 kDa, 5.85 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1980 bp, 660 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ycgB, ldh |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 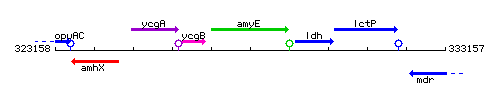
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU03040
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Endohydrolysis of (1->4)-alpha-D-glucosidic linkages in oligosaccharides and polysaccharides (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: glycosyl hydrolase 13 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: secreted (according to Swiss-Prot), extracellular (signal peptide) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 1BAG (complex with maltopentaose)
- UniProt: P00691
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.2.1.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP550 (cat), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Birgit Voigt, Haike Antelmann, Dirk Albrecht, Armin Ehrenreich, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Stefan Evers, Gerhard Gottschalk, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Thomas Schweder, Michael Hecker
Cell physiology and protein secretion of Bacillus licheniformis compared to Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2009, 16(1-2);53-68
[PubMed:18957862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
W L Nicholson, Y K Park, T M Henkin, M Won, M J Weickert, J A Gaskell, G H Chambliss
Catabolite repression-resistant mutations of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase promoter affect transcription levels and are in an operator-like sequence.
J Mol Biol: 1987, 198(4);609-18
[PubMed:3123701]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Takashi Inaoka, Kozo Ochi
Scandium stimulates the production of amylase and bacilysin in Bacillus subtilis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(22);8181-3
[PubMed:21948839]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)