CsrA
- Description: motility regulator, binds to the hag mRNA to inhibit its translation
| Gene name | csrA |
| Synonyms | yviG |
| Essential | no |
| Product | motility regulator |
| Function | control of hag translation |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CsrA | |
| MW, pI | 8 kDa, 6.09 |
| Gene length, protein length | 222 bp, 74 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | hag, fliW |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 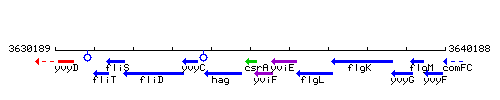
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CsrA regulon: hag
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35370
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family: csrA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 1T3O
- UniProt: P33911
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: csrA PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP469 (spc), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional Reviews: PubMed
Paul Babitzke, Carol S Baker, Tony Romeo
Regulation of translation initiation by RNA binding proteins.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2009, 63;27-44
[PubMed:19385727]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original Publications
Sampriti Mukherjee, Paul Babitzke, Daniel B Kearns
FliW and FliS function independently to control cytoplasmic flagellin levels in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(2);297-306
[PubMed:23144244]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sampriti Mukherjee, Helen Yakhnin, Dave Kysela, Josh Sokoloski, Paul Babitzke, Daniel B Kearns
CsrA-FliW interaction governs flagellin homeostasis and a checkpoint on flagellar morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 82(2);447-61
[PubMed:21895793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Helen Yakhnin, Pallavi Pandit, Tom J Petty, Carol S Baker, Tony Romeo, Paul Babitzke
CsrA of Bacillus subtilis regulates translation initiation of the gene encoding the flagellin protein (hag) by blocking ribosome binding.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 64(6);1605-20
[PubMed:17555441]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Prajna R Kulkarni, Xiaohui Cui, Joshua W Williams, Ann M Stevens, Rahul V Kulkarni
Prediction of CsrA-regulating small RNAs in bacteria and their experimental verification in Vibrio fischeri.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2006, 34(11);3361-9
[PubMed:16822857]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
B Soldo, V Lazarevic, C Mauël, D Karamata
Sequence of the 305 degrees-307 degrees region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 11);3079-88
[PubMed:8969505]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)