CheA
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, chemotactic signal modulator
| Gene name | cheA |
| Synonyms | cheN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | chemotactic signal modulator |
| MW, pI | 74 kDa, 4.452 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2013 bp, 671 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cheB, cheW |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 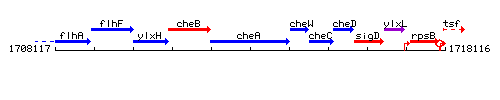
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein modification, transcription factors and their control, motility and chemotaxis, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, SigD regulon, Spo0A regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16430
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of CheY and CheB PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), localizes to the cell poles PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P29072
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- in minimal medium, CheA is present with 2,600 +/- 560 molecules per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Vincent J Cannistraro, George D Glekas, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
Cellular stoichiometry of the chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(13);3220-7
[PubMed:21515776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kang Wu, Hanna E Walukiewicz, George D Glekas, George W Ordal, Christopher V Rao
Attractant binding induces distinct structural changes to the polar and lateral signaling clusters in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
J Biol Chem: 2011, 286(4);2587-95
[PubMed:21098025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Travis J Muff, George W Ordal
The CheC phosphatase regulates chemotactic adaptation through CheD.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(47);34120-8
[PubMed:17908686]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Kazuo Kobayashi
Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(2);395-409
[PubMed:17850253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Werhane, P Lopez, M Mendel, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, L M Márquez-Magaña
The last gene of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis, ylxL, is required for maximal sigmaD function.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(12);4025-9
[PubMed:15175317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Patrick Eichenberger, José E González-Pastor, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 50(5);1683-701
[PubMed:14651647]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michael A Zimmer, Hendrik Szurmant, Michael M Saulmon, Marissa A Collins, Jason S Bant, George W Ordal
The role of heterologous receptors in McpB-mediated signalling in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(2);555-68
[PubMed:12123464]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Liam F Garrity, George W Ordal
Activation of the CheA kinase by asparagine in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143(Pt 9);2945-2951
[PubMed:12094812]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J R Kirby, C J Kristich, M M Saulmon, M A Zimmer, L F Garrity, I B Zhulin, G W Ordal
CheC is related to the family of flagellar switch proteins and acts independently from CheD to control chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 42(3);573-85
[PubMed:11722727]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Karatan, M M Saulmon, M W Bunn, G W Ordal
Phosphorylation of the response regulator CheV is required for adaptation to attractants during Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
J Biol Chem: 2001, 276(47);43618-26
[PubMed:11553614]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L F Garrity, S L Schiel, R Merrill, J Reizer, M H Saier, G W Ordal
Unique regulation of carbohydrate chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis by the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and the methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein McpC.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(17);4475-80
[PubMed:9721285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Estacio, S S Anna-Arriola, M Adedipe, L M Márquez-Magaña
Dual promoters are responsible for transcription initiation of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(14);3548-55
[PubMed:9657996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Rosario, G W Ordal
CheC and CheD interact to regulate methylation of Bacillus subtilis methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 21(3);511-8
[PubMed:8866475]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L M Márquez-Magaña, M J Chamberlin
Characterization of the sigD transcription unit of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(8);2427-34
[PubMed:8157612]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D K Fuhrer, G W Ordal
Bacillus subtilis CheN, a homolog of CheA, the central regulator of chemotaxis in Escherichia coli.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(23);7443-8
[PubMed:1938941]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)