CitZ
Revision as of 13:43, 8 December 2014 by Fabian Commichau (talk | contribs) (→Biological materials)
- Description: citrate synthase
| Gene name | citZ |
| Synonyms | citA2 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | citrate synthase II |
| Function | TCA cycle |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: citZ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CitZ | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: citZ | |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 5.451 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1116 bp, 372 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | icd, ytwI |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 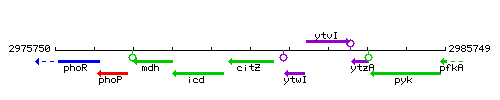
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29140
Phenotypes of a mutant
- glutamate auxotrophy and a defect in sporulation PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29140
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + H2O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: citrate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-284 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by acetyl-CoA, 2-oxoglutarate and NADH PubMed FEBS Letters
- Inhibited by citrate and CoA (competitively against acetyl-CoA and non-competitively against oxaloacetate) PubMed
- Inhibited by ATP competitively in B. subtilis strain 168 and HS 1A17 PubMed PubMed
- In B. subtilis strain HS 2A2, ATP inhibits a non-competitive fashion PubMed
- Activated by AMP PubMed
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (homogeneously distributed throughout the cell) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29140
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39120
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.3.1
Additional information
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of CitZ can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 8373 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 20578 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 22342 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 10224 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 18693 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP678 (erm), GP797 (spec) available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A999 ( citZ::spec), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GP790 (citZ-icd-mdh::kan), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP797 ( citZ::spec), allows expression of ''icd'' and ''mdh'', available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- pGP1120 (N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, purification from B. subtilis, in pGP380) (available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- pGP1776 (for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal Strep-tag, in pGP172, available in Jörg Stülke's lab)
- pGP1761 (expression with N-terminal His-tag from E. coli, in pWH844), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in Linc Sonenshein's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications