CheW
- Description: modulation of CheA activity in response to attractants, scaffold protein: facilitates coupling between CheA and receptors
| Gene name | cheW |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | CheA modulator |
| Function | control of CheA activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cheW | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 4.422 |
| Gene length, protein length | 468 bp, 156 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cheA, cheC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 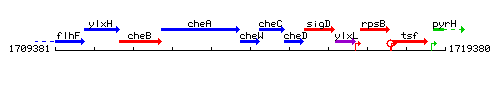
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed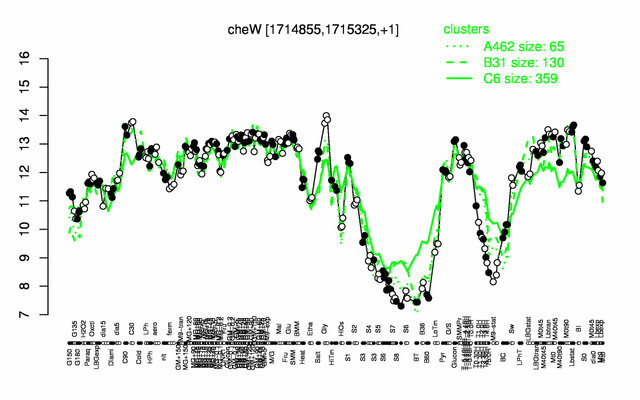
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, DegU regulon, SigD regulon, Spo0A regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16440
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16440
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): CheV (N-terminal domain)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
- predominantly present at the cell poles PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16440
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39802
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- in minimal medium, CheW is present with 2,100 +/- 430 molecules per cell PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 840 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1423 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1996 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1296 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 699 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Serena Mordini, Cecilia Osera, Simone Marini, Francesco Scavone, Riccardo Bellazzi, Alessandro Galizzi, Cinzia Calvio
The role of SwrA, DegU and P(D3) in fla/che expression in B. subtilis.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(12);e85065
[PubMed:24386445]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Vincent J Cannistraro, George D Glekas, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
Cellular stoichiometry of the chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(13);3220-7
[PubMed:21515776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kang Wu, Hanna E Walukiewicz, George D Glekas, George W Ordal, Christopher V Rao
Attractant binding induces distinct structural changes to the polar and lateral signaling clusters in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
J Biol Chem: 2011, 286(4);2587-95
[PubMed:21098025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kazuo Kobayashi
Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(2);395-409
[PubMed:17850253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Werhane, P Lopez, M Mendel, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, L M Márquez-Magaña
The last gene of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis, ylxL, is required for maximal sigmaD function.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(12);4025-9
[PubMed:15175317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michael W Bunn, George W Ordal
Receptor conformational changes enhance methylesterase activity during chemotaxis by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(3);721-8
[PubMed:14731274]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Patrick Eichenberger, José E González-Pastor, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 50(5);1683-701
[PubMed:14651647]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Estacio, S S Anna-Arriola, M Adedipe, L M Márquez-Magaña
Dual promoters are responsible for transcription initiation of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(14);3548-55
[PubMed:9657996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Rosario, K L Fredrick, G W Ordal, J D Helmann
Chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis requires either of two functionally redundant CheW homologs.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(9);2736-9
[PubMed:8169224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L M Márquez-Magaña, M J Chamberlin
Characterization of the sigD transcription unit of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(8);2427-34
[PubMed:8157612]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D W Hanlon, P B Carpenter, G W Ordal
Influence of attractants and repellents on methyl group turnover on methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Bacillus subtilis and role of CheW.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(13);4218-22
[PubMed:1624415]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D W Hanlon, L M Márquez-Magaña, P B Carpenter, M J Chamberlin, G W Ordal
Sequence and characterization of Bacillus subtilis CheW.
J Biol Chem: 1992, 267(17);12055-60
[PubMed:1601874]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)