SpoIIIE
- Description: ATP-dependent DNA translocase, transports the forespore chromosome across the sporulation septum
| Gene name | spoIIIE |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent DNA translocase required for chromosome
partitioning through the septum into the forespore |
| Function | chromosome partition during sporulation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIIE | |
| MW, pI | 86 kDa, 6.757 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2361 bp, 787 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ylzJ, ymfC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 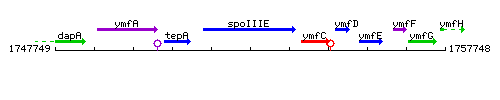
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed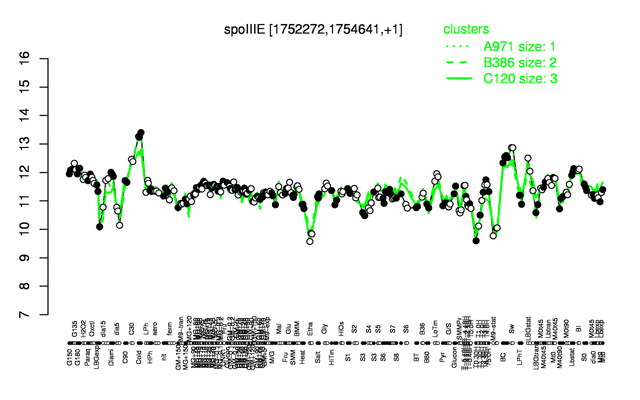
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA condensation/ segregation, sporulation/ other, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16800
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- transports the forespore chromosome across the sporulation septum PubMed
- translocates septum-entrapped DNA only when septum closure precedes complete segregation of chromosomes PubMed
- the two DNA translocases SftA and SpoIIIE synergistically affect chromosome dimer resolution presumably by positioning the dif sites in close proximity, before or after completion of cell division, respectively PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): SftA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- assembles into ∼45 nm complexes PubMed
- Localization:
- transmembrane domain mediates dynamic localization to active division sites PubMed
- complexes are recruited to nascent sites of septation, and are subsequently escorted by the constriction machinery to the center of sporulation and division septa PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P21458
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: spoIIIE PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Christine Kaimer, Peter L Graumann
Players between the worlds: multifunctional DNA translocases.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2011, 14(6);719-25
[PubMed:22047950]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Jean-Bernard Fiche, Diego I Cattoni, Nele Diekmann, Julio Mateos Langerak, Caroline Clerte, Catherine A Royer, Emmanuel Margeat, Thierry Doan, Marcelo Nöllmann
Recruitment, assembly, and molecular architecture of the SpoIIIE DNA pump revealed by superresolution microscopy.
PLoS Biol: 2013, 11(5);e1001557
[PubMed:23667326]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Diego I Cattoni, Osvaldo Chara, Cédric Godefroy, Emmanuel Margeat, Sonia Trigueros, Pierre-Emmanuel Milhiet, Marcelo Nöllmann
SpoIIIE mechanism of directional translocation involves target search coupled to sequence-dependent motor stimulation.
EMBO Rep: 2013, 14(5);473-9
[PubMed:23559069]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Kaimer, Katrin Schenk, Peter L Graumann
Two DNA translocases synergistically affect chromosome dimer resolution in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(6);1334-40
[PubMed:21239579]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tinya C Fleming, Jae Yen Shin, Sang-Hyuk Lee, Eric Becker, Kerwyn Casey Huang, Carlos Bustamante, Kit Pogliano
Dynamic SpoIIIE assembly mediates septal membrane fission during Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
Genes Dev: 2010, 24(11);1160-72
[PubMed:20516200]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David J Sherratt, Lidia K Arciszewska, Estelle Crozat, James E Graham, Ian Grainge
The Escherichia coli DNA translocase FtsK.
Biochem Soc Trans: 2010, 38(2);395-8
[PubMed:20298190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Kaimer, José Eduardo González-Pastor, Peter L Graumann
SpoIIIE and a novel type of DNA translocase, SftA, couple chromosome segregation with cell division in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 74(4);810-25
[PubMed:19818024]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Steven J Biller, William F Burkholder
The Bacillus subtilis SftA (YtpS) and SpoIIIE DNA translocases play distinct roles in growing cells to ensure faithful chromosome partitioning.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 74(4);790-809
[PubMed:19788545]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kathleen A Marquis, Briana M Burton, Marcelo Nollmann, Jerod L Ptacin, Carlos Bustamante, Sigal Ben-Yehuda, David Z Rudner
SpoIIIE strips proteins off the DNA during chromosome translocation.
Genes Dev: 2008, 22(13);1786-95
[PubMed:18593879]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jerod L Ptacin, Marcelo Nollmann, Eric C Becker, Nicholas R Cozzarelli, Kit Pogliano, Carlos Bustamante
Sequence-directed DNA export guides chromosome translocation during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2008, 15(5);485-93
[PubMed:18391964]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Briana M Burton, Kathleen A Marquis, Nora L Sullivan, Tom A Rapoport, David Z Rudner
The ATPase SpoIIIE transports DNA across fused septal membranes during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2007, 131(7);1301-12
[PubMed:18160039]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sigal Ben-Yehuda, David Z Rudner, Richard Losick
Assembly of the SpoIIIE DNA translocase depends on chromosome trapping in Bacillus subtilis.
Curr Biol: 2003, 13(24);2196-200
[PubMed:14680637]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
J Bath, L J Wu, J Errington, J C Wang
Role of Bacillus subtilis SpoIIIE in DNA transport across the mother cell-prespore division septum.
Science: 2000, 290(5493);995-7
[PubMed:11062134]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Wu, J Errington
Use of asymmetric cell division and spoIIIE mutants to probe chromosome orientation and organization in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 27(4);777-86
[PubMed:9515703]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Pogliano, A E Hofmeister, R Losick
Disappearance of the sigma E transcription factor from the forespore and the SpoIIE phosphatase from the mother cell contributes to establishment of cell-specific gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(10);3331-41
[PubMed:9150232]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Wu, J Errington
Septal localization of the SpoIIIE chromosome partitioning protein in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 1997, 16(8);2161-9
[PubMed:9155041]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M E Sharpe, J Errington
Postseptational chromosome partitioning in bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1995, 92(19);8630-4
[PubMed:7567988]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Wu, P J Lewis, R Allmansberger, P M Hauser, J Errington
A conjugation-like mechanism for prespore chromosome partitioning during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1995, 9(11);1316-26
[PubMed:7797072]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Wu, J Errington
Bacillus subtilis SpoIIIE protein required for DNA segregation during asymmetric cell division.
Science: 1994, 264(5158);572-5
[PubMed:8160014]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D Foulger, J Errington
The role of the sporulation gene spoIIIE in the regulation of prespore-specific gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1989, 3(9);1247-55
[PubMed:2507870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Panzer, R Losick, D Sun, P Setlow
Evidence for an additional temporal class of gene expression in the forespore compartment of sporulating Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(1);561-4
[PubMed:2492502]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P D Butler, J Mandelstam
Nucleotide sequence of the sporulation operon, spoIIIE, of Bacillus subtilis.
J Gen Microbiol: 1987, 133(9);2359-70
[PubMed:3129532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)