ResE
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Gene name | resE |
| Synonyms | ypxE |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: resE | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ResE | |
| MW, pI | 66 kDa, 5.344 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1767 bp, 589 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sigX, resD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 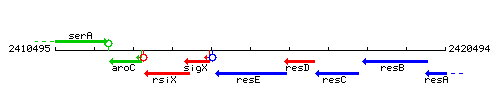
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed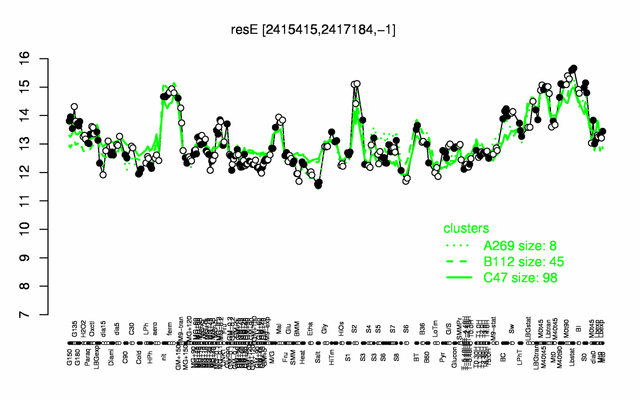
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
regulators of electron transport, protein modification, transcription factors and their control, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpA regulon, PhoP regulon, ResD regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23110
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of ResD
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification: autophosphorylation on a His residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P35164
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Michiko M Nakano, Hao Geng, Shunji Nakano, Kazuo Kobayashi
The nitric oxide-responsive regulator NsrR controls ResDE-dependent gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(16);5878-87
[PubMed:16885456]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Soo-Keun Choi, Milton H Saier
Mechanism of CcpA-mediated glucose repression of the resABCDE operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2006, 11(1-2);104-10
[PubMed:16825793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y Zhu
Involvement of ResE phosphatase activity in down-regulation of ResD-controlled genes in Bacillus subtilis during aerobic growth.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(6);1938-44
[PubMed:11222591]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S M Birkey, W Liu, X Zhang, M F Duggan, F M Hulett
Pho signal transduction network reveals direct transcriptional regulation of one two-component system by another two-component regulator: Bacillus subtilis PhoP directly regulates production of ResD.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 30(5);943-53
[PubMed:9988472]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y P Dailly, P Zuber, D P Clark
Characterization of anaerobic fermentative growth of Bacillus subtilis: identification of fermentation end products and genes required for growth.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(21);6749-55
[PubMed:9352926]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, P Zuber, P Glaser, A Danchin, F M Hulett
Two-component regulatory proteins ResD-ResE are required for transcriptional activation of fnr upon oxygen limitation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(13);3796-802
[PubMed:8682783]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Sun, E Sharkova, R Chesnut, S Birkey, M F Duggan, A Sorokin, P Pujic, S D Ehrlich, F M Hulett
Regulators of aerobic and anaerobic respiration in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(5);1374-85
[PubMed:8631715]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)