YsxC
Revision as of 14:31, 16 April 2012 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: assembly of the 50S subunit of the ribosome
| Gene name | ysxC |
| Synonyms | orfX |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | GTPase |
| Function | ribosome assembly |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: YsxC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 9.708 |
| Gene length, protein length | 585 bp, 195 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ysxD, lonA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 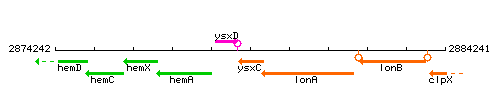
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
translation, essential genes, membrane proteins, GTP-binding proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28190
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Binds and hydrolyzes GTP and readily exchanges GDP for GTP
- Protein family: engB family (according to Swiss-Prot) Era/Obg family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P38424
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Naotake Ogasawara, Nara, Japan
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Natalie Verstraeten, Maarten Fauvart, Wim Versées, Jan Michiels
The universally conserved prokaryotic GTPases.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2011, 75(3);507-42, second and third pages of table of contents
[PubMed:21885683]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Robert A Britton
Role of GTPases in bacterial ribosome assembly.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2009, 63;155-76
[PubMed:19575570]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed