Difference between revisions of "Fur"
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>12029044, 19508286 , 12354229, 16672620, 19508285 , 18697947 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18487332,12374814,14563870,18697947,10400588,11790741,16672620,12207695,9701813,12029044,,17725565,17012385,12950915,12029044, 19508286 , 12354229, 16672620, 19508285 , 18697947 </pubmed> |
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 22:50, 13 June 2009
- Description: transcription regulator of iron homoeostasis
| Gene name | fur |
| Synonyms | yqkL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional repressor |
| Function | regulation of iron homoeostasis
and transcription of ferri-siderophore uptake genes |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 5.374 |
| Gene length, protein length | 447 bp, 149 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ripX, spoIIM |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 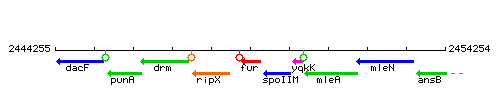
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23520
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Fur family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Genes controlled by Fur
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P54574
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: fur
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
John Helmann, Cornell University, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References