Difference between revisions of "CitZ"
Cadu Cunha (talk | contribs) (→Extended information on the protein) |
Cadu Cunha (talk | contribs) (→Extended information on the protein) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| − | * '''Kinetic information:''' Michaelis-Menten [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | + | * '''Kinetic information:''' Michaelis-Menten (Random Sequential Reaction Mechanism) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] |
* '''Domains:''' | * '''Domains:''' | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
** Inhibited by acetyl-CoA [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ** Inhibited by acetyl-CoA [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ||
** Inhibited by citrate and CoA (competitively against acetyl-CoA and non-competitively against oxaloacetate) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ** Inhibited by citrate and CoA (competitively against acetyl-CoA and non-competitively against oxaloacetate) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ||
| − | ** Inhibited by ATP [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4980242 PubMed] | + | ** Inhibited by ATP competitively in ''B. subtilis'' strain 168 and HS 1A17 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4980242 PubMed] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] |
| + | *** In ''B. subtilis'' strain HS 2A2, ATP inhibits in a non-competitive fashion [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** Activated by AMP [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/4211224 PubMed] | ||
* '''Interactions:''' | * '''Interactions:''' | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 10 June 2009
- Description: citrate synthase
| Gene name | citZ |
| Synonyms | citA2 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | citrate synthase II |
| Function | TCA cycle |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 5.451 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1116 bp, 372 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ytwI, icd |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 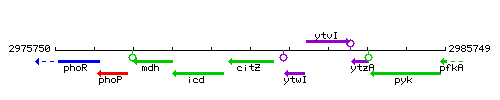
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29140
Phenotypes of a mutant
glutamate auxotrophy and a defect in sporulation PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + H2O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: citrate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Michaelis-Menten (Random Sequential Reaction Mechanism) PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-284 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by acetyl-CoA PubMed
- Inhibited by citrate and CoA (competitively against acetyl-CoA and non-competitively against oxaloacetate) PubMed
- Inhibited by ATP competitively in B. subtilis strain 168 and HS 1A17 PubMed PubMed
- In B. subtilis strain HS 2A2, ATP inhibits in a non-competitive fashion PubMed
- Activated by AMP PubMed
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 2C6X
- Swiss prot entry: P39120
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.3.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation: repressed by glucose (6.7-fold) (CcpA) PubMed, catabolite repression (CcpA), repression by glucose + glutamate (CcpC) PubMed, repression under anaerobic conditions PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: CcpA: transcription repression, CcpA: transcription repression, CcpC: transcription repression PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP678 (erm), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody: available in Linc Sonenshein lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hyun-Jin Kim, Agnes Roux, Abraham L Sonenshein
Direct and indirect roles of CcpA in regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(1);179-90
[PubMed:12100558]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, P Zuber, A L Sonenshein
Anaerobic regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(13);3304-11
[PubMed:9642180]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Jin, A L Sonenshein
Identification of two distinct Bacillus subtilis citrate synthase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4669-79
[PubMed:8045898]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Blencke et al. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways. Metab Eng. 5: 133-149 PubMed
- Macek et al. (2007) The serine/ threonine/ tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6: 697-707 PubMed
- Kim HJ, Roux A, Sonenshein AL (2002b) Direct and indirect roles of CcpA in regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes. Mol Microbiol 45:179-190. PubMed
- Nakano MM, Zuber P, Sonenshein AL (1998) Anaerobic regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes. J Bacteriol. 180: 3304-3311. PubMed
- Jin S, Sonenshein AL (1994) Identification of two distinct Bacillus subtilis citrate synthase genes J Bacteriol. 176: 4669-4679. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed