Difference between revisions of "CsaA"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
| − | <pubmed> 10658654, 10816431 , 13129613 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 17372352, 10658654, 10816431 , 13129613 </pubmed> |
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 5 June 2009
- Description: molecular chaperone involved in protein secretion
| Gene name | csaA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | molecular chaperone |
| Function | protein secretion |
| MW, pI | 11 kDa, 8.691 |
| Gene length, protein length | 330 bp, 110 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | bsrF, yobQ |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 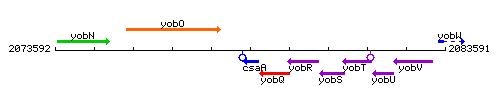
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU19040
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Secretion associated chaperone. Assumed functional analogue of E. coli SecB
- Protein family: FIG1 subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure: 2NZO
- Swiss prot entry: P37584
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: Pspac-csaA PubMed
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Yuliya A Shapova, Mark Paetzel
Crystallographic analysis of Bacillus subtilis CsaA.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr: 2007, 63(Pt 4);478-85
[PubMed:17372352]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Dirk Linde, Rudolf Volkmer-Engert, Sandra Schreiber, Jörg P Müller
Interaction of the Bacillus subtilis chaperone CsaA with the secretory protein YvaY.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2003, 226(1);93-100
[PubMed:13129613]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J P Müller, J Ozegowski, S Vettermann, J Swaving, K H Van Wely, A J Driessen
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis CsaA with SecA and precursor proteins.
Biochem J: 2000, 348 Pt 2(Pt 2);367-73
[PubMed:10816431]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
Jörg P Müller, Sierd Bron, Gerard Venema, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Chaperone-like activities of the CsaA protein of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2000, 146 ( Pt 1);77-88
[PubMed:10658654]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed