Difference between revisions of "YraA"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 02:16, 3 June 2009
- Description: general stress protein, degradation of damaged thiol-containing proteins
| Gene name | yraA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | cysteine proteinase |
| Function | degradation of damaged thiol-containing proteins |
| MW, pI | 18 kDa, 4.729 |
| Gene length, protein length | 507 bp, 169 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | adhA, sacC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 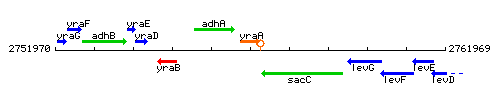
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: peptidase C56 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YfkM
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: O06006
- KEGG entry: BSU27020
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Höper et al. (2005) Comprehensive Characterization of the Contribution of Individual SigB-Dependent General Stress Genes to Stress Resistance of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bact. 187: 2810-2826 PubMed
- Jervis et al. 2007. SigM-responsive genes of Bacillus subtilis and their promoters. J. Bacteriol. 189: 4534-4538. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed