Difference between revisions of "YjbH"
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
* '''Operon:''' | * '''Operon:''' | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:16, 8 April 2009
- Description: stimulation of Spx degradation
| Gene name | yjbH |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | stimulation of Spx degradation |
| MW, pI | 31 kDa, 5.206 |
| Gene length, protein length | 825 bp, 275 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pepF, yjbI |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 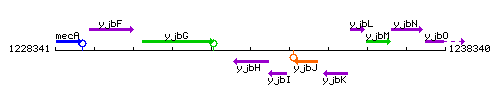
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: adaptor protein for ClpXP-catalyzed Spx degradation PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):contains Zn atoms (coordinated by the N-terminal His-rich region) PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity: Zn atom is released upon treatment with strong oxidants PubMed
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Peter Zuber, Oregon Health and Science University, USA Homepage
Claes von Wachenfeldt, Lund University, Sweden Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Garg et al. 2009. The YjbH protein of Bacillus subtilis enhances ClpXP-catalyzed proteolysis of Spx. J. Bacteriol. 191: 1268-1277. PubMed
- Larsson, J. T., A. Rogstam, and C. von Wachenfeldt. 2007. YjbH is a novel negative effector of the disulphide stress regulator, Spx, in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 66:669-684. PubMed