Difference between revisions of "TyrS"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
<pubmed>19258532,10546897 </pubmed> | <pubmed>19258532,10546897 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>9098057,12547201,11842119,10943892,9282752,8045882,8348614,1735721,8289305,20110252 , 21333656 15378759 25733610</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>9098057,12547201,11842119,10943892,9282752,8045882,8348614,1735721,8289305,20110252 , 21333656 15378759 25733610 25733611</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 4 March 2015
- Description: tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (major)
| Gene name | tyrS |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (major) |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: tyrS | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: tyrS | |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 5.213 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1266 bp, 422 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rpsD, ytzK |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 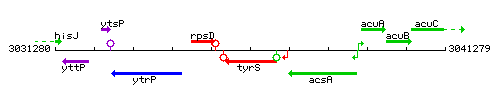
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed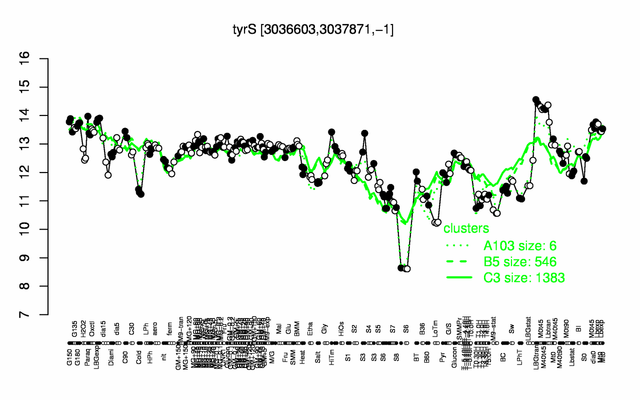
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
translation, essential genes, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29670
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- the gene can be deleted, but the mutant acquires suppressors in dtrR to allow expression of tyrZ PubMed
- a tyrS tyrZ double mutant is not viable PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29670
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29670
- Structure:
- UniProt: P22326
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- T-box: RNA switch, transcriptional antitermination PubMed
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 848 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 3406 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 4314 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1369 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1521 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Sara A Leiman, Charles Richardson, Lucy Foulston, Alexander K W Elsholz, Eric A First, Richard Losick
Identification and characterization of mutations conferring resistance to D-amino acids in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2015, 197(9);1632-9
[PubMed:25733611]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Rebecca N Williams-Wagner, Frank J Grundy, Medha Raina, Michael Ibba, Tina M Henkin
The Bacillus subtilis tyrZ gene encodes a highly selective tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase and is regulated by a MarR regulator and T box riboswitch.
J Bacteriol: 2015, 197(9);1624-31
[PubMed:25733610]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jiachen Wang, Edward P Nikonowicz
Solution structure of the K-turn and Specifier Loop domains from the Bacillus subtilis tyrS T-box leader RNA.
J Mol Biol: 2011, 408(1);99-117
[PubMed:21333656]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jiachen Wang, Tina M Henkin, Edward P Nikonowicz
NMR structure and dynamics of the Specifier Loop domain from the Bacillus subtilis tyrS T box leader RNA.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(10);3388-98
[PubMed:20110252]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Melinda S Gerdeman, Tina M Henkin, Jennifer V Hines
Solution structure of the Bacillus subtilis T-box antiterminator RNA: seven nucleotide bulge characterized by stacking and flexibility.
J Mol Biol: 2003, 326(1);189-201
[PubMed:12547201]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Melinda S Gerdeman, Tina M Henkin, Jennifer V Hines
In vitro structure-function studies of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS mRNA antiterminator: evidence for factor-independent tRNA acceptor stem binding specificity.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2002, 30(4);1065-72
[PubMed:11842119]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
F J Grundy, J A Collins, S M Rollins, T M Henkin
tRNA determinants for transcription antitermination of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene.
RNA: 2000, 6(8);1131-41
[PubMed:10943892]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S M Rollins, F J Grundy, T M Henkin
Analysis of cis-acting sequence and structural elements required for antitermination of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 25(2);411-21
[PubMed:9282752]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, S E Hodil, S M Rollins, T M Henkin
Specificity of tRNA-mRNA interactions in Bacillus subtilis tyrS antitermination.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(8);2587-94
[PubMed:9098057]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, S M Rollins, T M Henkin
Interaction between the acceptor end of tRNA and the T box stimulates antitermination in the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene: a new role for the discriminator base.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4518-26
[PubMed:8045882]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
Conservation of a transcription antitermination mechanism in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and amino acid biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria.
J Mol Biol: 1994, 235(2);798-804
[PubMed:8289305]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
tRNA as a positive regulator of transcription antitermination in B. subtilis.
Cell: 1993, 74(3);475-82
[PubMed:8348614]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T M Henkin, B L Glass, F J Grundy
Analysis of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene: conservation of a regulatory sequence in multiple tRNA synthetase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(4);1299-306
[PubMed:1735721]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)