Difference between revisions of "SubtiPathways"
Raphael2215 (talk | contribs) (→tRNA charging) |
Raphael2215 (talk | contribs) (→Phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
=== [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/index.php?pathway=lysi Lysine, threonine] === | === [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/index.php?pathway=lysi Lysine, threonine] === | ||
| − | === [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ | + | === [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/index.php?pathway=tryp Phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan] === |
=== [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/index.php?pathway=prol Proline] === | === [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/index.php?pathway=prol Proline] === | ||
Revision as of 13:59, 30 January 2014
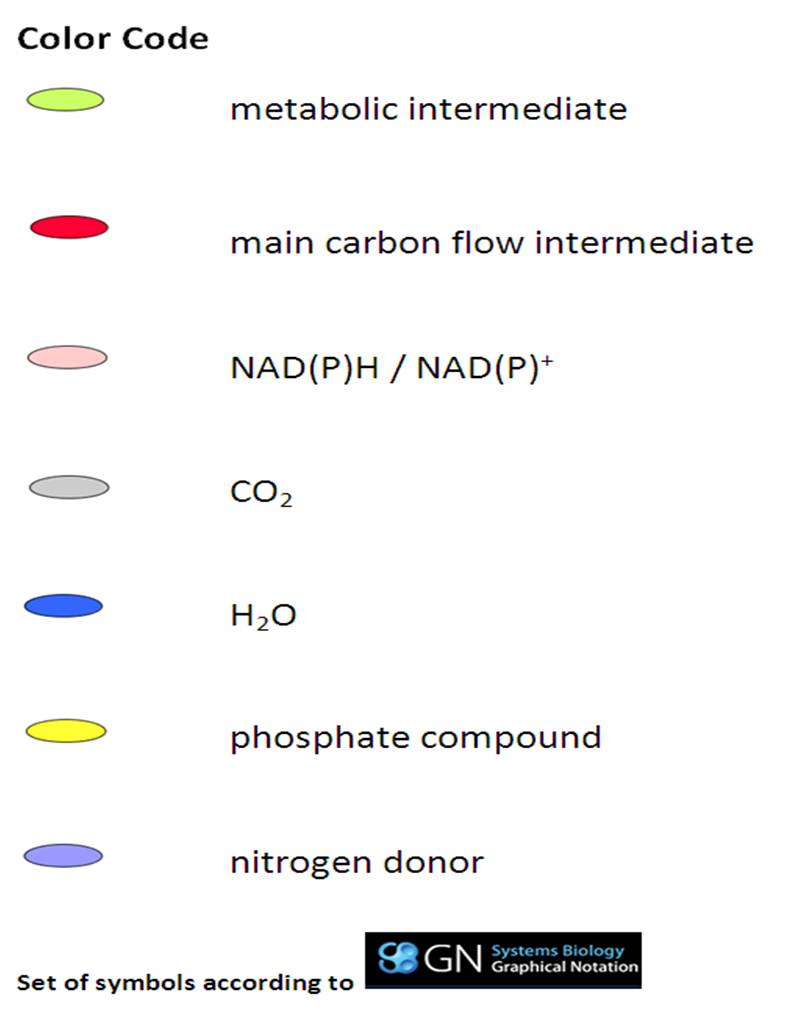
SubtiPathways is a model of B. subtilis metabolism and regulation in SBML/SBGN (Systems Biology Markup Language/ Graphical Notation). There is a color code for key metabolites (see the legend on the right side).
It can be used like Google Maps (scroll and zoom to the pathways). The markers of proteins and compounds listed on the right side in each pathway are containing links to the corresponding SubtiWiki and PubChem pages, respectively. There is a short description for each protein in the bubbles, too.
Contact: General Microbiology, University of Göttingen, send mail
Now online: A description of SubtiWiki, SubtiPathways, and SubtInteract in the 2012 Database issue of Nucleic Acids Research
A collection of important papers on B. subtilis metabolism can be found here
Carbon metabolism
Central carbon metabolism
Utilization of different carbon sources
Nitrogen and amino acid metabolism
Ammonium assimilation and glutamate metabolism (incl. glutamine and arginine)
Alanine, glycine, serine
Aspartate, asparagine
Cysteine, methionine
Histidine
Isoleucine, valine, leucine
Lysine, threonine
Phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Proline
Utilization of other nitrogen sources
Lipid metabolism
Fatty acid and phospholipid biosynthesis
Fatty acid degradation
Nucleotides
Gene regulation of nucleotide metabolism
Nucleoside catabolism
Purine biosynthesis
Purine catabolism
Purine salvage pathways
Pyrimidine metabolism
Metabolism of cofactors
CoA synthesis
Folate biosynthesis
Menaquinone
Riboflavin and FAD synthesis
Thiamin synthesis
Biotin synthesis
Other pathways
Cell wall
Murein recycling
Stress responses
Phosphorelay
Sulfate assimilation
tRNA charging
Biofilm formation
Protein secretion
metal ion homeostasis
Publications describing SubtiWiki and SubtiPathways