Difference between revisions of "UgtP"
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
| Line 142: | Line 141: | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
** pGP2571, for expression in ''B. subtilis'' (based on [[pBQ200]], available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab | ** pGP2571, for expression in ''B. subtilis'' (based on [[pBQ200]], available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab | ||
| − | ** pGP2600, for expression/ purification from ''E. coli'' with N-terminal | + | ** pGP2600, for expression/ purification from ''E. coli'' with N-terminal Strep-tag, in [[pGP172]], available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''lacZ fusion:''' | * '''lacZ fusion:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 30 January 2014
- Description: UDP-glucose diacylglycerol glucosyltransferase, growth-rate dependent inhibitor of cell division
| Gene name | ugtP |
| Synonyms | ypfP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | UDP-glucose diacylglycerol glucosyltransferase |
| Function | synthesis of glycolipids and anchoring of lipoteichoic acid, inhibition of FtsZ assembly |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ugtP | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: UgtP | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: ugtP | |
| MW, pI | 43 kDa, 8.398 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1146 bp, 382 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | metA, cspD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 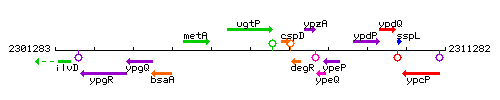
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, lipid metabolism/ other, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU21920
Phenotypes of a mutant
- cells are bent and distended PubMed
- increased expression of the SigM, SigV, and SigX regulons PubMed
- altered localization of MreB (irregular clusters instead of helical dots) PubMed
- the inactivation of ugtP suppresses the poor and filametous growth of the yvcL zapA double mutant PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- UDP-glucose + 1,2-diacylglycerol = UDP + 1,2-diacyl-3-(O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (according to Swiss-Prot)
- the interaction with FtsZ results in inhibition of cell division and an increase of cell size PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane-bound protein, self-assembles into tightly wound spirals in vitro PubMed
- under nutrient rich conditions (increased concentration of UDP-Glc): throughout the cell, concentrated at the cell poles and/or the cytokinetic ring, interaction with FtsZ PubMed
- under nutrient poor conditions: forms punctate foci (oligomers), no interaction with FtsZ PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54166
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP1369 (ugtP::spc), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- pGP2571, for expression in B. subtilis (based on pBQ200, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- pGP2600, for expression/ purification from E. coli with N-terminal Strep-tag, in pGP172, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
An-Chun Chien, Norbert S Hill, Petra Anne Levin
Cell size control in bacteria.
Curr Biol: 2012, 22(9);R340-9
[PubMed:22575476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David W Adams, Jeff Errington
Bacterial cell division: assembly, maintenance and disassembly of the Z ring.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(9);642-53
[PubMed:19680248]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Daisuke Shiomi, William Margolin
A sweet sensor for size-conscious bacteria.
Cell: 2007, 130(2);216-8
[PubMed:17662935]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications