Difference between revisions of "RsbR"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/index.php?protein=RsbR RbsR] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/interact/index.php?protein=RsbR RbsR] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/search.php?enzyme=rsbR rsbR]''' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 30 kDa, 4.731 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 30 kDa, 4.731 | ||
Revision as of 10:11, 7 January 2014
- Description: activator of RsbT kinase activity, stressosome sensor protein
| Gene name | rsbR |
| Synonyms | ycxR, rsbRA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | activator of RsbT kinase activity, stressosome sensor protein |
| Function | control of SigB activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rsbR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RbsR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: rsbR | |
| MW, pI | 30 kDa, 4.731 |
| Gene length, protein length | 822 bp, 274 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ndoA, rsbS |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 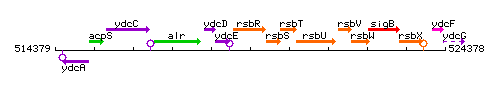
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
sigma factors and their control, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU04670
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- RsbRA is composed of an N-terminal nonheme globin domain and a highly conserved C-terminal STAS (Sulphate Transporter and AntiSigma factor antagonist) domain. The C-terminal STAS domain is the target of the serine/threonine-specific kinase RsbT (see below).
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- component of the stressosome
Database entries
- UniProt: P42409
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Bill Haldenwang, San Antonio, USA
- Chet Price, Davis, USA homepage
- Rick Lewis, Newcastle, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Articles
Additional publications: PubMed
Tatiana A Gaidenko, Xiaomei Bie, Enoch P Baldwin, Chester W Price
Substitutions in the presumed sensing domain of the Bacillus subtilis stressosome affect its basal output but not response to environmental signals.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(14);3588-97
[PubMed:21602359]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Adam Reeves, Luis Martinez, William Haldenwang
Expression of, and in vivo stressosome formation by, single members of the RsbR protein family in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2010, 156(Pt 4);990-998
[PubMed:20019076]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jon Marles-Wright, Tim Grant, Olivier Delumeau, Gijs van Duinen, Susan J Firbank, Peter J Lewis, James W Murray, Joseph A Newman, Maureen B Quin, Paul R Race, Alexis Rohou, Willem Tichelaar, Marin van Heel, Richard J Lewis
Molecular architecture of the "stressosome," a signal integration and transduction hub.
Science: 2008, 322(5898);92-6
[PubMed:18832644]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Katrin Gronau, Anja Klutzny, Michael Hecker
Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(19);3509-26
[PubMed:17726680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Adam Reeves, W G Haldenwang
Isolation and characterization of dominant mutations in the Bacillus subtilis stressosome components RsbR and RsbS.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(5);1531-41
[PubMed:17158665]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shrin Kuo, Shuyu Zhang, Robyn L Woodbury, W G Haldenwang
Associations between Bacillus subtilis sigmaB regulators in cell extracts.
Microbiology (Reading): 2004, 150(Pt 12);4125-36
[PubMed:15583165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Chien-Cheng Chen, Michael D Yudkin, Olivier Delumeau
Phosphorylation and RsbX-dependent dephosphorylation of RsbR in the RsbR-RsbS complex of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(20);6830-6
[PubMed:15466036]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tae-Jong Kim, Tatiana A Gaidenko, Chester W Price
In vivo phosphorylation of partner switching regulators correlates with stress transmission in the environmental signaling pathway of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(18);6124-32
[PubMed:15342582]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tae-Jong Kim, Tatiana A Gaidenko, Chester W Price
A multicomponent protein complex mediates environmental stress signaling in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2004, 341(1);135-50
[PubMed:15312768]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Chien-Cheng Chen, Richard J Lewis, Robin Harris, Michael D Yudkin, Olivier Delumeau
A supramolecular complex in the environmental stress signalling pathway of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(6);1657-69
[PubMed:12950928]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Zhang, J M Scott, W G Haldenwang
Loss of ribosomal protein L11 blocks stress activation of the Bacillus subtilis transcription factor sigma(B).
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(7);2316-21
[PubMed:11244072]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Scott, J Ju, T Mitchell, W G Haldenwang
The Bacillus subtilis GTP binding protein obg and regulators of the sigma(B) stress response transcription factor cofractionate with ribosomes.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(10);2771-7
[PubMed:10781545]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T A Gaidenko, X Yang, Y M Lee, C W Price
Threonine phosphorylation of modulator protein RsbR governs its ability to regulate a serine kinase in the environmental stress signaling pathway of Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 288(1);29-39
[PubMed:10329124]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Akbar, C M Kang, T A Gaidenko, C W Price
Modulator protein RsbR regulates environmental signalling in the general stress pathway of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 24(3);567-78
[PubMed:9179850]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Voelker, A Voelker, W G Haldenwang
The yeast two-hybrid system detects interactions between Bacillus subtilis sigmaB regulators.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(23);7020-3
[PubMed:8955331]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Yang, C M Kang, M S Brody, C W Price
Opposing pairs of serine protein kinases and phosphatases transmit signals of environmental stress to activate a bacterial transcription factor.
Genes Dev: 1996, 10(18);2265-75
[PubMed:8824586]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Voelker, A Voelker, W G Haldenwang
Reactivation of the Bacillus subtilis anti-sigma B antagonist, RsbV, by stress- or starvation-induced phosphatase activities.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(18);5456-63
[PubMed:8808936]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C M Kang, M S Brody, S Akbar, X Yang, C W Price
Homologous pairs of regulatory proteins control activity of Bacillus subtilis transcription factor sigma(b) in response to environmental stress.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(13);3846-53
[PubMed:8682789]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Dufour, U Voelker, A Voelker, W G Haldenwang
Relative levels and fractionation properties of Bacillus subtilis σ(B) and its regulators during balanced growth and stress.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(13);3701-9 sigma
[PubMed:8682769]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A A Wise, C W Price
Four additional genes in the sigB operon of Bacillus subtilis that control activity of the general stress factor sigma B in response to environmental signals.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(1);123-33
[PubMed:8002610]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)