Difference between revisions of "Rny"
(→Reviews) |
|||
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed>21957024 22568516</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>21957024 22568516 24064983 </pubmed> |
==Publications on ''B. subtilis rny''== | ==Publications on ''B. subtilis rny''== | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 13 November 2013
- Description: RNase Y, 5' end sensitive endoribonuclease, involved in the degradation/processing of mRNA
| Gene name | rny |
| Synonyms | ymdA |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | RNase Y |
| Function | RNA processing and degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rny | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Rny | |
| Regulatory function of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 58,7 kDa, 5.39 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1560 bp, 520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | pbpX, ymdB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed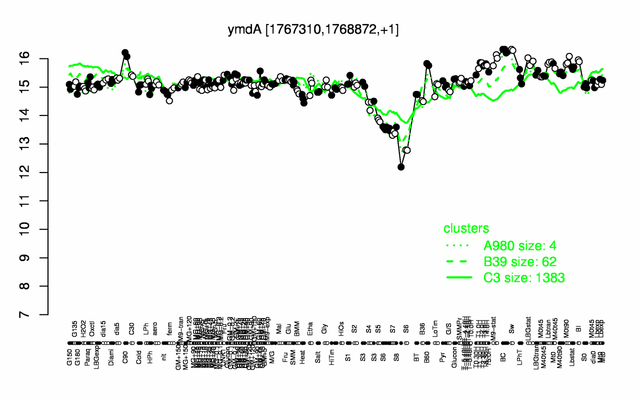
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
Rnases, biofilm formation, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Targets of RNase Y
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16960
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- transcription profile resulting from rny depletion: GEO PubMed
- defect in spore germination PubMed
- a study from the lab of Ciaran Condon reports that rny is non-essential and that the mutant is strongly impaired in sporulation, genetic competence and many other phenotypes PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- RNase Y cleaves S-box riboswitch RNAs in vivo and in vitro PubMed
- preference for 5' monophosphorylated substrate in vitro PubMed
- endonucleolytic cleavage PubMed
- required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA PubMed
- cleavage activity appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure PubMed
- RNase Y initiates the degradation of rpsO mRNA PubMed
- RNase Y is responsible for the degradation of 23S rRNA, 16S rRNA, and mRNAs in aging spores PubMed
- Protein family: Member of the HD superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases; 2',3' cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): requires Mg+2, which can be replaced by Zn+2 or Mn+2 ions, PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity: appears sensitive to downstream secondary structure, PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31774
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.1.4.16
Additional information
required for the processing of the gapA operon mRNA
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: constitutive
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- essential!!!!
- 4043 (rny under p-spac control, cat), GP193 (rny under p-xyl control, cat), both available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- SSB447 (rny under P-spac control, "erm") available in Putzer lab.
- Expression vector:
- N-terminal Strep-tag, expression in E. coli, in pGP172: pGP441, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP380: pGP775, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- C-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP382: pGP1852, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression of RNase Y missing the N-terminal transmembrane domain (25aa) as an intein fusion in E. coli (no tag left in the purified protein) available in the Putzer lab
- wild type rny, expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1201, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- there is also a series of domain constructs present in pBQ200, all available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- chromosomal expression of Rny-Strep, spc: GP1033, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP459 (in pAC7), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- B. subtilis 3569 (amyE:: (p-xyl rny-gfpmut1-spc)), available in Errington lab
- pGP1368 for chromosomal expression of rny-YFP, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct: GP1030 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody: available in van Dijl and in Jörg Stülke's lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Harald Putzer, IBPC Paris, France Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Soumaya Laalami, Léna Zig, Harald Putzer
Initiation of mRNA decay in bacteria.
Cell Mol Life Sci: 2014, 71(10);1799-828
[PubMed:24064983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Richard J Lewis, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Stülke
RNA degradation in Bacillus subtilis: an interplay of essential endo- and exoribonucleases.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 84(6);1005-17
[PubMed:22568516]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David H Bechhofer
Bacillus subtilis mRNA decay: new parts in the toolkit.
Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA: 2011, 2(3);387-94
[PubMed:21957024]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Publications on B. subtilis rny
Sabine Figaro, Sylvain Durand, Laetitia Gilet, Nadège Cayet, Martin Sachse, Ciarán Condon
Bacillus subtilis mutants with knockouts of the genes encoding ribonucleases RNase Y and RNase J1 are viable, with major defects in cell morphology, sporulation, and competence.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(10);2340-8
[PubMed:23504012]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Soumaya Laalami, Philippe Bessières, Anna Rocca, Léna Zig, Pierre Nicolas, Harald Putzer
Bacillus subtilis RNase Y activity in vivo analysed by tiling microarrays.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(1);e54062
[PubMed:23326572]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frank Bürmann, Prachi Sawant, Marc Bramkamp
Identification of interaction partners of the dynamin-like protein DynA from Bacillus subtilis.
Commun Integr Biol: 2012, 5(4);362-9
[PubMed:23060960]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sylvain Durand, Laetitia Gilet, Philippe Bessières, Pierre Nicolas, Ciarán Condon
Three essential ribonucleases-RNase Y, J1, and III-control the abundance of a majority of Bacillus subtilis mRNAs.
PLoS Genet: 2012, 8(3);e1002520
[PubMed:22412379]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Einat Segev, Yoav Smith, Sigal Ben-Yehuda
RNA dynamics in aging bacterial spores.
Cell: 2012, 148(1-2);139-49
[PubMed:22209493]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph A Newman, Lorraine Hewitt, Cecilia Rodrigues, Alexandra S Solovyova, Colin R Harwood, Richard J Lewis
Dissection of the network of interactions that links RNA processing with glycolysis in the Bacillus subtilis degradosome.
J Mol Biol: 2012, 416(1);121-36
[PubMed:22198292]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, Jamie Richards, Joel G Belasco, David H Bechhofer
Decay of a model mRNA in Bacillus subtilis by a combination of RNase J1 5' exonuclease and RNase Y endonuclease activities.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6384-6
[PubMed:21908660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gintaras Deikus, David H Bechhofer
5' End-independent RNase J1 endonuclease cleavage of Bacillus subtilis model RNA.
J Biol Chem: 2011, 286(40);34932-40
[PubMed:21862575]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Diethmaier, Nico Pietack, Katrin Gunka, Christoph Wrede, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Christina Herzberg, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke
A novel factor controlling bistability in Bacillus subtilis: the YmdB protein affects flagellin expression and biofilm formation.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(21);5997-6007
[PubMed:21856853]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Patrice Bruscella, Karen Shahbabian, Soumaya Laalami, Harald Putzer
RNase Y is responsible for uncoupling the expression of translation factor IF3 from that of the ribosomal proteins L35 and L20 in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1526-41
[PubMed:21843271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Marc Schaffer, Ulrike Mäder, Christine Diethmaier, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1459-73
[PubMed:21815947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Joseph Newman, Fabian M Rothe, Alexandra S Solovyova, Cecilia Rodrigues, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis: a Natively disordered protein that is the functional equivalent of RNase E from Escherichia coli.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(19);5431-41
[PubMed:21803996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Henrike Pförtner, Leonie Rempeters, Nico Pietack, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
The RNA degradosome in Bacillus subtilis: identification of CshA as the major RNA helicase in the multiprotein complex.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 77(4);958-71
[PubMed:20572937]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, David H Bechhofer
Initiation of decay of Bacillus subtilis rpsO mRNA by endoribonuclease RNase Y.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(13);3279-86
[PubMed:20418391]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jessica C Zweers, Thomas Wiegert, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Stress-responsive systems set specific limits to the overproduction of membrane proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2009, 75(23);7356-64
[PubMed:19820159]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Karen Shahbabian, Ailar Jamalli, Léna Zig, Harald Putzer
RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO J: 2009, 28(22);3523-33
[PubMed:19779461]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Fabian M Rothe, Christina Herzberg, Eva Wagner, Daniel Hellwig, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Elke Hammer, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2009, 8(6);1350-60
[PubMed:19193632]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alison Hunt, Joy P Rawlins, Helena B Thomaides, Jeff Errington
Functional analysis of 11 putative essential genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2006, 152(Pt 10);2895-2907
[PubMed:17005971]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Publications on homologs from other organisms
Song Ok Kang, Michael G Caparon, Kyu Hong Cho
Virulence gene regulation by CvfA, a putative RNase: the CvfA-enolase complex in Streptococcus pyogenes links nutritional stress, growth-phase control, and virulence gene expression.
Infect Immun: 2010, 78(6);2754-67
[PubMed:20385762]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Makiko Nagata, Chikara Kaito, Kazuhisa Sekimizu
Phosphodiesterase activity of CvfA is required for virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(4);2176-84
[PubMed:17951247]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Chikara Kaito, Kenji Kurokawa, Yasuhiko Matsumoto, Yutaka Terao, Shigetada Kawabata, Shigeyuki Hamada, Kazuhisa Sekimizu
Silkworm pathogenic bacteria infection model for identification of novel virulence genes.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 56(4);934-44
[PubMed:15853881]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)