Difference between revisions of "CitZ"
(→Biological materials) |
(→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP678 (erm), GP797 (spec) available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''Mutant:''' GP678 (erm), GP797 (spec) available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
** 1A999 ( ''citZ''::''spec''), {{PubMed| }}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A999&Search=1A999 BGSC] | ** 1A999 ( ''citZ''::''spec''), {{PubMed| }}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A999&Search=1A999 BGSC] | ||
| + | ** GP790 (''citz, icd, mdh''::''kan''), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 13 August 2013
- Description: citrate synthase
| Gene name | citZ |
| Synonyms | citA2 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | citrate synthase II |
| Function | TCA cycle |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: citZ | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CitZ | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 5.451 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1116 bp, 372 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | icd, ytwI |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 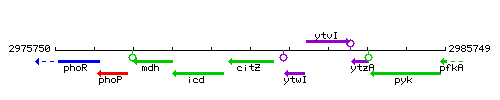
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29140
Phenotypes of a mutant
glutamate auxotrophy and a defect in sporulation PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + H2O + oxaloacetate = citrate + CoA (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: citrate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Michaelis-Menten (Random Sequential Reaction Mechanism) PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-284 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by acetyl-CoA, 2-oxoglutarate and NADH PubMed FEBS Letters
- Inhibited by citrate and CoA (competitively against acetyl-CoA and non-competitively against oxaloacetate) PubMed
- Inhibited by ATP competitively in B. subtilis strain 168 and HS 1A17 PubMed PubMed
- In B. subtilis strain HS 2A2, ATP inhibits a non-competitive fashion PubMed
- Activated by AMP PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39120
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.3.1
Additional information
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of CitZ can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP678 (erm), GP797 (spec) available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A999 ( citZ::spec), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GP790 (citz, icd, mdh::kan), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- pGP1120 (N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, purification from B. subtilis, in pGP380) (available in Stülke lab)
- pGP1776 (for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal Strep-tag, in pGP172, available in Stülke lab)
- pGP1761 (expression with N-terminal His-tag from E. coli, in pWH844), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody: available in Linc Sonenshein lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
G Wiegand, S J Remington
Citrate synthase: structure, control, and mechanism.
Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem: 1986, 15;97-117
[PubMed:3013232]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Kieran B Pechter, Frederik M Meyer, Alisa W Serio, Jörg Stülke, Abraham L Sonenshein
Two roles for aconitase in the regulation of tricarboxylic acid branch gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(7);1525-37
[PubMed:23354745]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frederik M Meyer, Jan Gerwig, Elke Hammer, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Physical interactions between tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a metabolon.
Metab Eng: 2011, 13(1);18-27
[PubMed:20933603]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hyun-Jin Kim, Agnes Roux, Abraham L Sonenshein
Direct and indirect roles of CcpA in regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(1);179-90
[PubMed:12100558]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Jourlin-Castelli, N Mani, M M Nakano, A L Sonenshein
CcpC, a novel regulator of the LysR family required for glucose repression of the citB gene in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2000, 295(4);865-78
[PubMed:10656796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Matsuno, T Blais, A W Serio, T Conway, T M Henkin, A L Sonenshein
Metabolic imbalance and sporulation in an isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(11);3382-91
[PubMed:10348849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, P Zuber, A L Sonenshein
Anaerobic regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(13);3304-11
[PubMed:9642180]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Jin, A L Sonenshein
Characterization of the major citrate synthase of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(12);3658-60
[PubMed:8655569]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Jin, A L Sonenshein
Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis citrate synthase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4680-90
[PubMed:8045899]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Jin, A L Sonenshein
Identification of two distinct Bacillus subtilis citrate synthase genes.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4669-79
[PubMed:8045898]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D E Johnson, R S Hanson
Bacterial citrate synthases: purification, molecular weight and kinetic mechanism.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 1974, 350(2);336-53
[PubMed:4211224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V R Flechtner, R S Hanson
Coarse and fine control of citrate synthase from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 1969, 184(2);252-62
[PubMed:4980242]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)