Difference between revisions of "DivIVA"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' cell-division initiation protein (septum placement), part of the Min system (with [[MinC]], [[MinD]], [[MinJ]]), [[Noc]] and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring [[FtsZ|Z ring]] placement <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' curvature sensitive membrane binding protein that recruits other proteins to the poles and the division septum, cell-division initiation protein (septum placement), part of the Min system (with [[MinC]], [[MinD]], [[MinJ]]), [[Noc]] and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring [[FtsZ|Z ring]] placement <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' DivIVA is required for polar localisation of | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' |
| + | ** curvature sensitive membrane binding protein that recruits other proteins to the poles and the division septum | ||
| + | ** DivIVA is required for polar localisation of [[MinC]]-[[MinD]] via [[MinJ]]. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19019154 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** It also recruits [[RacA]] to the distal pole of the prespore [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12493822 PubMed]. | ||
* '''Protein family:''' gpsB family (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' gpsB family (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| Line 79: | Line 82: | ||
* '''Kinetic information:''' | * '''Kinetic information:''' | ||
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''Domains:''' |
| − | + | ** the first 60 amino acids constitute a conserved lipid binding domain. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19478798 PubMed] | |
| + | ** the C-terminal domain is less conserved | ||
| + | ** multimerisation involves two coiled-coil motifs, one in the lipid binding domain, and the other one being present in the helical C-terminal domain [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18388125 PubMed]. | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| Line 92: | Line 97: | ||
* '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | * '''[[SubtInteract|Interactions]]:''' | ||
| − | ** ([[MinC]]-[[MinD]])-[[MinJ]]-[[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|20352045}} | + | ** ([[MinC]]-[[MinD]])-[[MinJ]]-[[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|20352045}}, [[MinJ]] binds to the N-terminal lipid-binding domain of [[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|23264578}} |
| − | ** [[DivIVA]]-[[RacA]], | + | ** [[DivIVA]]-[[RacA]], [[RacA]] binds to the C-terminal domain of [[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|23264578}} |
| + | ** [[DivIVA]]-[[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|23264578}} | ||
** [[Maf]]-[[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|21564336}} | ** [[Maf]]-[[DivIVA]] {{PubMed|21564336}} | ||
** [[DivIVA]]-[[ComN]] {{PubMed|22582279}} | ** [[DivIVA]]-[[ComN]] {{PubMed|22582279}} | ||
| Line 156: | Line 162: | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>22582279, 19654604, 19666580,9219999,19019154,15554965, 12368265,11445541,10835369,12511520,14651647, 19478798 ,19429628, 11445541, 9219999, 9045828 20352045 20502438 11886553 21564336 22108385 22457634 22517742 22661688 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>22582279, 19654604, 19666580,9219999,19019154,15554965, 12368265,11445541,10835369,12511520,14651647, 19478798 ,19429628, 11445541, 9219999, 9045828 20352045 20502438 11886553 21564336 22108385 22457634 22517742 22661688 23264578 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 3 January 2013
- Description: curvature sensitive membrane binding protein that recruits other proteins to the poles and the division septum, cell-division initiation protein (septum placement), part of the Min system (with MinC, MinD, MinJ), Noc and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring Z ring placement
| Gene name | divIVA |
| Synonyms | ylmJ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | cell-division initiation protein |
| Function | septum placement |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: divIVA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DivIVA | |
| MW, pI | 19 kDa, 4.846 |
| Gene length, protein length | 492 bp, 164 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ylmH, ileS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 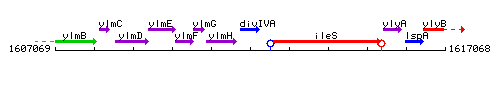
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15420
Phenotypes of a mutant
Deletion of divIVA leads to filamentation and polar divisions that in turn cause a minicell phenotype. PubMed A divIVA mutant has a severe sporulation defect. PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
Filamentation is suppressed by mutations in minCD PubMed.
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: gpsB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): GpsB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): not known
- Effectors of protein activity: not known
Database entries
- UniProt: P71021
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: divIVA PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: divIVA::tet available from the Hamoen Lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: divIVA-gfp fusions available from the Hamoen Lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Centre for Bacterial Cell Biology, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom [4]
Imrich Barak, Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications