Difference between revisions of "CodV"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* '''Locus tag:''' BSU16140 | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU16140 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=codV_1687187_1688101_1 Expression] | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 09:28, 25 January 2012
- Description: site-specific integrase/recombinase
| Gene name | codV |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | site-specific integrase/recombinase |
| Function | chromosome partitioning |
| MW, pI | 35 kDa, 9.31 |
| Gene length, protein length | 912 bp, 304 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trmFO, clpQ |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 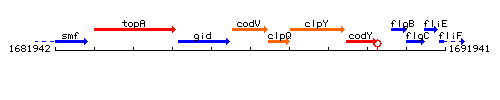
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16140
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: resolution of chromosome dimers by site specific recombination at the dif site (located close to the terminus region on the chromosome)
- Protein family: XerC subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): RipX
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
- assembles on the chromosome at the dif site throughout the cell cycle PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39776
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Christine Kaimer, Katrin Schenk, Peter L Graumann
Two DNA translocases synergistically affect chromosome dimer resolution in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(6);1334-40
[PubMed:21239579]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexandra E Bloor, Rocky M Cranenburgh
An efficient method of selectable marker gene excision by Xer recombination for gene replacement in bacterial chromosomes.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2006, 72(4);2520-5
[PubMed:16597952]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, P Serror, K W Wong, A L Sonenshein
Bacillus subtilis CodY represses early-stationary-phase genes by sensing GTP levels.
Genes Dev: 2001, 15(9);1093-103
[PubMed:11331605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S A Sciochetti, P J Piggot, G W Blakely
Identification and characterization of the dif Site from Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(3);1058-68
[PubMed:11208805]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S A Sciochetti, P J Piggot, D J Sherratt, G Blakely
The ripX locus of Bacillus subtilis encodes a site-specific recombinase involved in proper chromosome partitioning.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(19);6053-62
[PubMed:10498718]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Slack, P Serror, E Joyce, A L Sonenshein
A gene required for nutritional repression of the Bacillus subtilis dipeptide permease operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 15(4);689-702
[PubMed:7783641]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)