Difference between revisions of "GntP"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|20817675}} | |
| − | <pubmed>3011959,8288545,3037520,2537826,3020045,10746760,8370661, | + | <pubmed>3011959,8288545,3037520,2537826,3020045,10746760,8370661 ,1659648</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 16 April 2011
- Description: gluconate permease
| Gene name | gntP |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | gluconate permease |
| Function | gluconate uptake |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 8.098 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1344 bp, 448 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | gntK, gntZ |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 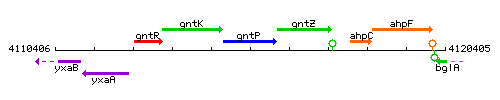
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transporters/ other, utilization of specific carbon sources, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40070
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: gntP permease family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YojA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P12012
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Ken-Ichi Yoshida, Izumi Ishio, Eishi Nagakawa, Yoshiyuki Yamamoto, Mami Yamamoto, Yasutaro Fujita
Systematic study of gene expression and transcription organization in the gntZ-ywaA region of the Bacillus subtilis genome.
Microbiology (Reading): 2000, 146 ( Pt 3);573-579
[PubMed:10746760]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Fujita, Y Miwa
Catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis gnt operon mediated by the CcpA protein.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(2);511-3
[PubMed:8288545]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Miwa, Y Fujita
Promoter-independent catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis gnt operon.
J Biochem: 1993, 113(6);665-71
[PubMed:8370661]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Reizer, J Deutscher, M H Saier, J Reizer
Analysis of the gluconate (gnt) operon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1991, 5(5);1081-9
[PubMed:1659648]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Fujita, T Fujita
Effect of mutations causing gluconate kinase or gluconate permease deficiency on expression of the Bacillus subtilis gnt operon.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(3);1751-4
[PubMed:2537826]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Fujita, T Fujita
The gluconate operon gnt of Bacillus subtilis encodes its own transcriptional negative regulator.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1987, 84(13);4524-8
[PubMed:3037520]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Fujita, T Fujita, Y Miwa, J Nihashi, Y Aratani
Organization and transcription of the gluconate operon, gnt, of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 1986, 261(29);13744-53
[PubMed:3020045]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
Y Fujita, J Nihashi, T Fujita
The characterization and cloning of a gluconate (gnt) operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Gen Microbiol: 1986, 132(1);161-9
[PubMed:3011959]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)