Difference between revisions of "XynC"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
<pubmed>20735481 </pubmed> | <pubmed>20735481 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>19407387,, 18957862, 17028274 | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|20817675}} |
| + | <pubmed>19407387,21256135 , 18957862, 17028274 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 19 February 2011
- Description: endo-xylanase, preference for methylglucurono-xylan
| Gene name | xynC |
| Synonyms | ynfF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | endo-xylanase |
| Function | xylan degradation |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 9.078 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1266 bp, 422 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ynfE, xynD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 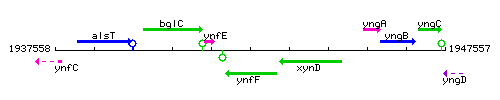
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18150
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Endohydrolysis of (1->4)-beta-D-xylosyl links in some glucuronoarabinoxylans (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: glycosyl hydrolase 30 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: secreted (according to Swiss-Prot), extracellular (signal peptide) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 3GTN
- UniProt: Q45070
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 3.2.1.136
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Franz J St John, Jason C Hurlbert, John D Rice, James F Preston, Edwin Pozharski
Ligand bound structures of a glycosyl hydrolase family 30 glucuronoxylan xylanohydrolase.
J Mol Biol: 2011, 407(1);92-109
[PubMed:21256135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Franz J St John, David K Godwin, James F Preston, Edwin Pozharski, Jason C Hurlbert
Crystallization and crystallographic analysis of Bacillus subtilis xylanase C.
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun: 2009, 65(Pt 5);499-503
[PubMed:19407387]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Birgit Voigt, Haike Antelmann, Dirk Albrecht, Armin Ehrenreich, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Stefan Evers, Gerhard Gottschalk, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Thomas Schweder, Michael Hecker
Cell physiology and protein secretion of Bacillus licheniformis compared to Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2009, 16(1-2);53-68
[PubMed:18957862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Franz J St John, John D Rice, James F Preston
Characterization of XynC from Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis strain 168 and analysis of its role in depolymerization of glucuronoxylan.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(24);8617-26
[PubMed:17028274]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)