Difference between revisions of "AbrB"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of gene expression during the transition <br/>from growth to stationary phase | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of gene expression during the transition <br/>from growth to stationary phase | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/biofilm.html Biofilm], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/histidine.html His], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/aspartate_asparagine.html Asp, Asn], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/phosphorelay.html Phosphorelay], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/glutamate.html Ammonium/ glutamate],<br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbon_flow.html Central C-metabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbohydrate_metabolic_pathways.html Sugar catabolism]''' | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/biofilm.html Biofilm], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/histidine.html His], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/aspartate_asparagine.html Asp, Asn], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/phosphorelay.html Phosphorelay], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/glutamate.html Ammonium/ glutamate],<br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbon_flow.html Central C-metabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbohydrate_metabolic_pathways.html Sugar catabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/other_nitrogen_sources/index.html Alternative nitrogen sources]''' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 10 kDa, 6.57 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 10 kDa, 6.57 | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 11 December 2010
- Description: transcriptional regulator of transition state genes
| Gene name | abrB |
| Synonyms | cpsX, tolB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | regulation of gene expression during the transition from growth to stationary phase |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm, His, Asp, Asn, Phosphorelay, Ammonium/ glutamate, Central C-metabolism, Sugar catabolism, Alternative nitrogen sources | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 6.57 |
| Gene length, protein length | 282 bp, 94 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yabC, metS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 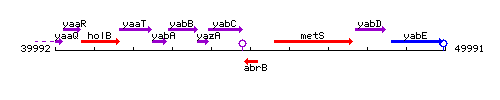
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The AbrB regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00370
Phenotypes of a mutant
No swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylated on Ser-86 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P08874
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: abrB PubMed
- Regulation: expressed at the onset of stationary phase PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: TT731 (aphA3)
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard Univ., Cambridge, USA homepage
Mark Strauch, Baltimore, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional publications: PubMed
The AbrB regulon
Other original publications
Additional publications: PubMed