Difference between revisions of "PpaC"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphate metabolism]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[essential genes]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | |||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
| Line 51: | Line 58: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
Revision as of 01:18, 9 December 2010
- Description: inorganic pyrophosphatase
| Gene name | ppaC |
| Synonyms | yybQ |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | inorganic pyrophosphatase |
| Function | recovery of phosphate ions from pyrophosphate |
| MW, pI | 33 kDa, 4.513 |
| Gene length, protein length | 927 bp, 309 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yybR, yybP |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 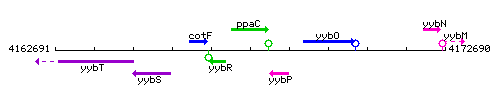
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphate metabolism, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40550
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Diphosphate + H2O = 2 phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: PPase class C family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: S-cysteinylation after diamide stress (C158) PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P37487
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.6.1.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: ppaC (according to DBTBS)
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dierk-Christoph Pöther, Dörte Becher, John D Helmann, Michael Hecker
S-cysteinylation is a general mechanism for thiol protection of Bacillus subtilis proteins after oxidative stress.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(36);25981-5
[PubMed:17611193]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Igor P Fabrichniy, Lari Lehtiö, Anu Salminen, Anton B Zyryanov, Alexander A Baykov, Reijo Lahti, Adrian Goldman
Structural studies of metal ions in family II pyrophosphatases: the requirement for a Janus ion.
Biochemistry: 2004, 43(45);14403-11
[PubMed:15533045]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A N Parfenyev, A Salminen, P Halonen, A Hachimori, A A Baykov, R Lahti
Quaternary structure and metal ion requirement of family II pyrophosphatases from Bacillus subtilis, Streptococcus gordonii, and Streptococcus mutans.
J Biol Chem: 2001, 276(27);24511-8
[PubMed:11342544]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Shintani, T Uchiumi, T Yonezawa, A Salminen, A A Baykov, R Lahti, A Hachimori
Cloning and expression of a unique inorganic pyrophosphatase from Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a new family of enzymes.
FEBS Lett: 1998, 439(3);263-6
[PubMed:9845334]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tom W Young, Nicholas J Kuhn, Albert Wadeson, Simon Ward, Dan Burges, G Dunstan Cooke
Bacillus subtilis ORF yybQ encodes a manganese-dependent inorganic pyrophosphatase with distinctive properties: the first of a new class of soluble pyrophosphatase?
Microbiology (Reading): 1998, 144 ( Pt 9);2563-2571
[PubMed:9782505]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N J Kuhn, S Ward
Purification, properties, and multiple forms of a manganese-activated inorganic pyrophosphatase from Bacillus subtilis.
Arch Biochem Biophys: 1998, 354(1);47-56
[PubMed:9633597]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)