Difference between revisions of "SacP"
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
<pubmed>10627040 12107147 3122206 2163394 8702561 2120236, </pubmed> | <pubmed>10627040 12107147 3122206 2163394 8702561 2120236, </pubmed> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 21 July 2009
- Description: trigger enzyme: sucrose-specific phosphotransferase system, EIIBC component
| Gene name | sacP |
| Synonyms | ipa-49d |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: sucrose-specific phosphotransferase system, EIIBC component |
| Function | sucrose uptake and phosphorylation, control of SacT activity |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 49 kDa, 7.026 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1383 bp, 461 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sacA, ywcJ |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 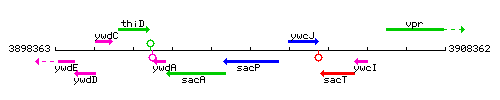
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38050
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: PTS permease, sucrose permease (Scr) family PubMed
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05306
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.69
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism: CcpA: transcription repression
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jonathan Reizer, Steffi Bachem, Aiala Reizer, Maryvonne Arnaud, Milton H Saier, Jörg Stülke
Novel phosphotransferase system genes revealed by genome analysis - the complete complement of PTS proteins encoded within the genome of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1999, 145 ( Pt 12);3419-3429
[PubMed:10627040]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Arnaud, M Débarbouillé, G Rapoport, M H Saier, J Reizer
In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 1996, 271(31);18966-72
[PubMed:8702561]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S L Sutrina, P Reddy, M H Saier, J Reizer
The glucose permease of Bacillus subtilis is a single polypeptide chain that functions to energize the sucrose permease.
J Biol Chem: 1990, 265(30);18581-9
[PubMed:2120236]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
M Debarbouille, M Arnaud, A Fouet, A Klier, G Rapoport
The sacT gene regulating the sacPA operon in Bacillus subtilis shares strong homology with transcriptional antiterminators.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);3966-73
[PubMed:2163394]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Fouet, M Arnaud, A Klier, G Rapoport
Bacillus subtilis sucrose-specific enzyme II of the phosphotransferase system: expression in Escherichia coli and homology to enzymes II from enteric bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1987, 84(24);8773-7
[PubMed:3122206]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)