Difference between revisions of "WalK"
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
* '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q45614 Q45614] | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q45614 Q45614] | ||
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU40400] |
* '''E.C. number:''' | * '''E.C. number:''' | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 25 June 2009
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, controls cell wall metabolism
| Gene name | walK |
| Synonyms | yycG |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase (OmpR family) |
| Function | control of cell wall metabolism |
| MW, pI | 69 kDa, 4.775 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1833 bp, 611 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yycH, walR |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 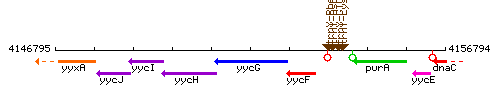
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40400
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot), part of the division septum in growing cells PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: Q45614
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: expressed during vegetative growth, repressed during stationary phase PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References