Difference between revisions of "IlvB"
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' repressed by casamino acids [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12107147 PubMed], repressed by [[CodY]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed], expressed in the absence of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose (CcpA) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.ntnrih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed], during growth repressed under nitrogen limiting conditions ([[TnrA]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15547269 PubMed] | * '''Regulation:''' repressed by casamino acids [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12107147 PubMed], repressed by [[CodY]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed], expressed in the absence of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose (CcpA) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.ntnrih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed], during growth repressed under nitrogen limiting conditions ([[TnrA]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15547269 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** repressed during growth in the presence of branched chain amino acids ([[CodY]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' glucose regulation: [[CcpA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed], [[TnrA]]: transcription repession [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15547269 PubMed], repression by BCAA: tRNA-controlled RNA switch (T-box) that mediates termination/antitermination, [[CodY]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18083814 PubMed2] | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' glucose regulation: [[CcpA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12193635 PubMed], [[TnrA]]: transcription repession [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15547269 PubMed], repression by BCAA: tRNA-controlled RNA switch (T-box) that mediates termination/antitermination, [[CodY]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18083814 PubMed2] | ||
| + | ** [[CodY]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12618455 PubMed] | ||
* '''Additional information:''' subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | * '''Additional information:''' subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 11 June 2009
- Description: acetolactate synthase (large subunit)
| Gene name | ilvB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetolactate synthase (large subunit) |
| Function | biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids |
| MW, pI | 62 kDa, 5.178 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1722 bp, 574 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ilvH, ysnD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 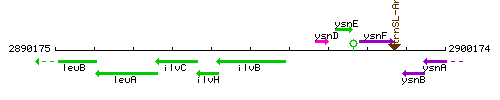
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28310
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 pyruvate = 2-acetolactate + CO2 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: TPP enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 1N53 (T box RNA)
- Swiss prot entry: P37251
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.2.1.6
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: repressed by casamino acids PubMed, repressed by CodY PubMed, expressed in the absence of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose (CcpA) PubMed, during growth repressed under nitrogen limiting conditions (TnrA) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: glucose regulation: CcpA PubMed, TnrA: transcription repession PubMed, repression by BCAA: tRNA-controlled RNA switch (T-box) that mediates termination/antitermination, CodY: transcription repression PubMed1 PubMed2
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP324, ilvB under control of pXyl (cat), available in Jörg Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Mäder et al. (2002) Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis of Bacillus subtilis Gene Expression Modulated by Amino Acid Availability. J. Bacteriol 184: 1844288-4295 PubMed
- Gerth et al. (2008) Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 190:321-331 PubMed
- Grandoni, J. A., S. A. Zahler, and J. M. Calvo. 1992. Transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 174:3212-3219. PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Meinken, C., Matin, A. & Stülke, J. (2002) Insufficient expression of the ilv-leu operon encoding enzymes of branched-chain amino acids biosynthesis limits growth of a Bacillus subtilis ccpA mutant. J. Bacteriol. 184: 5174-5178. PubMed
- Shivers RP, Sonenshein AL: Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons. Mol Microbiol 2005, 56:1549-1559. PubMed
- Tojo S, Satomura T, Morisaki K, Deutscher J, Hirooka K, Fujita Y: Elaborate transcription regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through global regulators of CcpA, CodY and TnrA. Mol Microbiol 2005, 56:1560-1573. PubMed
- Tojo S, Satomura T, Morisaki K, Yoshida KI, Hirooka K, Fujita Y: Negative transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon for biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through the Bacillus subtilis global regulator TnrA. J Bacteriol 2004, 186:7971-7979. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed