Difference between revisions of "CodY"
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 2 June 2009
- Description: regulation of a large regulon in response to branched-chain amino acid limitation
| Gene name | codY |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional pleiotropic repressor |
| Function | regulation of a large regulon in response to
branched-chain amino acid limitation to the presence of branched-chain amino acids |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 4.75 |
| Gene length, protein length | 777 bp, 259 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | clpY, flgB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 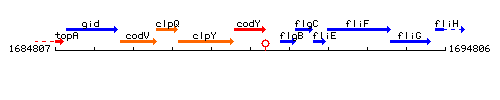
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag:
Phenotypes of a mutant
No swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: codY family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes/ operons controlled by CodY
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-215 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: P39779
- KEGG entry: BSU16170
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Tony Wilkinson, York University, U.K. homepage
Oscar Kuipers, University of Groningen, The Netherlands Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Macek et al. (2007) The serine/ threonine/ tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6: 697-707 PubMed
- Kim, H. J., S. I. Kim, M. Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, K. Tachikawa, A. L. Sonenshein, and M. Strauch. (2003) Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene. J. Bacteriol. 185:1672-1680. PubMed
- Hamze et al. (2009) Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC. Microbiology 155: 398-412. PubMed
- Molle V, Nakura Y, Shivers RP, Yamaguchi H, Losick R, Fujita Y, Sonenshein AL: Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis. J Bacteriol 2003, 185:1911-1922. PubMed
- Sonenshein AL: CodY, a global regulator of stationary phase and virulence in Gram-positive bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 2005, 8:203-207. PubMed
- Ratnayake-Lecamwasam M, Serror P, Wong KW, Sonenshein AL: Bacillus subtilis CodY represses early-stationary-phase genes by sensing GTP levels. Genes Dev 2001, 15:1093-1103.PubMed
- Shivers RP, Sonenshein AL: Activation of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY by direct interaction with branched-chain amino acids. Mol Microbiol 2004, 53:599-611. PubMed
- Serror P, Sonenshein AL: Interaction of CodY, the novel Bacillus subtilis DNA-binding protein, with the dpp promoter region. Mol Microbiol 1996, 20:843-852. PubMed
- Joseph P, Ratnayake-Lecamwasam M, Sonenshein AL: A region of Bacillus subtilis CodY protein required for interaction with DNA. J Bacteriol 2005, 187:4127-4139. PubMed
- Shivers RP, Sonenshein AL: Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons. Mol Microbiol 2005, 56:1549-1559. PubMed
- Tojo S, Satomura T, Morisaki K, Deutscher J, Hirooka K, Fujita Y: Elaborate transcription regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through global regulators of CcpA, CodY and TnrA. Mol Microbiol 2005, 56:1560-1573. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed