Difference between revisions of "LicB"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:licB_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:licB_context.gif]] | ||
| + | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 23 March 2009
- Description: trigger enzyme: lichenan-specific phosphotransferase system, EIIB component
| Gene name | licB |
| Synonyms | celA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: lichenan-specific phosphotransferase system, EIIB component |
| Function | lichenan uptake and phosphorylation, control of LicR activity |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 6.314 |
| Gene length, protein length | 306 bp, 102 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | licC, licR |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 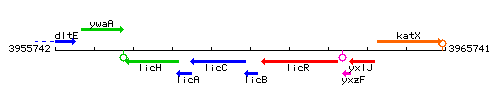
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-37 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.69
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: carbon catabolite repression, induction by oligomeric ß-glucosides PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: catabolite repression: repression by CcpA, induction: transcription activation by the PRD-type regulator LicR PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Macek et al. (2007) The serine/ threonine/ tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6: 697-707 PubMed
- Tobisch, S., P. Glaser, S. Krüger, and M. Hecker. 1997. Identification and characterization of a new ß-glucoside utilization system in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 179:496-506. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed