Difference between revisions of "CssS"
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
* '''Swiss prot entry:''' | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' | ||
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+BSU33020] |
* '''E.C. number:''' | * '''E.C. number:''' | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 19 March 2009
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, control of cellular responses to protein secretion stress
| Gene name | cssS |
| Synonyms | yvqB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase (OmpR family) |
| Function | control of cellular responses to protein secretion stress |
| MW, pI | 51 kDa, 5.795 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1353 bp, 451 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cssR, yuxN |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
| Caution: The sequence for this gene in SubtiList contains errors | |
Genetic context 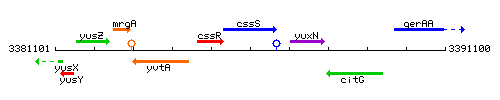
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two transmembrane segments, C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Hyyryläinen HL, Bolhuis A, Darmon E, Muukkonen L, Koski P, Vitikainen M, Sarvas M, Prágai Z, Bron S, van Dijl JM, Kontinen VP. (2001) A novel two-component regulatory system in Bacillus subtilis for the survival of severe secretion stress. Mol Microbiol. Sep;41(5): 1159-72. PubMed