Difference between revisions of "PycA"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
<pubmed>18613815 12769720 10229653 9597748 7780827 </pubmed> | <pubmed>18613815 12769720 10229653 9597748 7780827 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>18763711, 20081037 24825009</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>18763711, 20081037 24825009 25755103</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 30 July 2015
- Description: pyruvate carboxylase
| Gene name | pycA |
| Synonyms | ylaP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | pyruvate carboxylase |
| Function | replenishment of the oxaloacetate pool |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pycA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: pycA | |
| MW, pI | 127 kDa, 5.407 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3444 bp, 1148 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsW, ctaA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 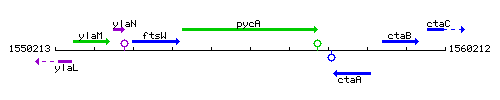
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14860
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactors: biotin
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14860
- Structure: 3BG5 (S. aureus)
- UniProt: Q9KWU4
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.4.1.1
Additional information
PycA binds to StrepTactin, and may be co-purified when purifying Strep-tagged proteins by SPINE.
PycA is subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- subject to positive stringent control upon lysine starvation PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- stringent response: due to presence of adenines at +1 and +2 positions of the transcript PubMed
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2222 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 6831 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1602 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 907 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2037 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP793 (cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications