Difference between revisions of "SecA"
(→References) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>19933328, 19924216, 18923516,12873133, 12242434,1385592,10816431,19850053,9880811, 12218047 17981983 9882663 23484952 20574771 23167435 23794293 23852076 24592260 24786965 11021932 7851746 7894702 10074074 8497195 8440733 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>19933328, 19924216, 18923516,12873133, 12242434,1385592,10816431,19850053,9880811, 12218047 17981983 9882663 23484952 20574771 23167435 23794293 23852076 24592260 24786965 11021932 7851746 7894702 10074074 8497195 8440733 7706219 7642557 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 22 June 2014
- Description: preprotein translocase subunit (ATPase), required for membrane targeting of DivIVA, motor protein that drives preprotein translocation through the SecY-SecE-SecG channel
| Gene name | secA |
| Synonyms | div, div-341, ts-341 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | preprotein translocase subunit (ATPase) |
| Function | protein secretion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: secA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SecA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: SecA | |
| MW, pI | 95 kDa, 5.34 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2523 bp, 841 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | prfB, yvyD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 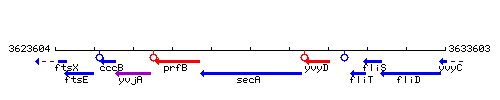
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
protein secretion, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35300
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35300
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: SecA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): none in Bacillus, some species have a paralogous secA gene named secA2 that has an altered substrate range
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: nucleotide binding domain, preprotein binding domain, IRA2 domain, scaffold domain, wing domain, IRA1 domain, C-terminal domain
- Modification:
- Cofactors: Mg
- Effectors of protein activity: anionic phospholipids, preprotein, SecY, signal peptides (even when added in trans) PubMed
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35300
- UniProt: P28366
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 945 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2829 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 411 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 395 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 564 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References