Difference between revisions of "KatA"
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1347 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1347 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 452 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 452 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 3140 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4640 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 7391 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 17 April 2014
- Description: main vegetative catalase 1
| Gene name | katA |
| Synonyms | kat-19 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | vegetative catalase |
| Function | detoxification (degradation) of hydrogen peroxide |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: katA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: katA | |
| MW, pI | 54 kDa, 6.151 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1449 bp, 483 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | senS, ssuB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 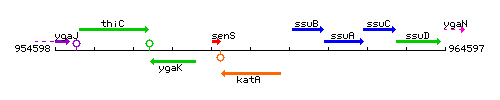
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed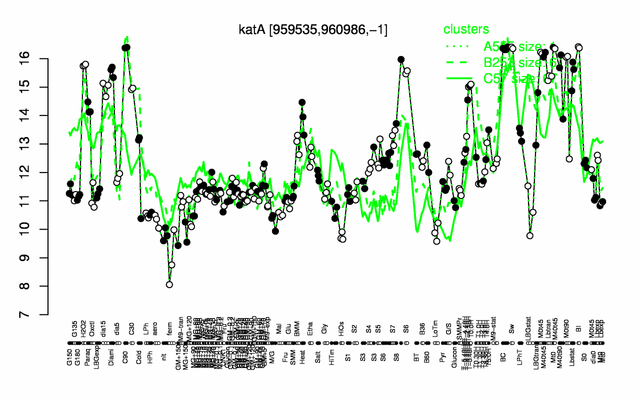
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
resistance against oxidative and electrophile stress, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU08820
Phenotypes of a mutant
- increased sensitivity to oxidative stress PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU08820
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 H2O2 = O2 + 2 H2O (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: catalase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-366 PubMed
- Cofactor(s): contains an iron-sulfur cluster, heme
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU08820
- Structure: 1SI8 (enzyme from Enterococcus faecalis, 68% identity)
- UniProt: P26901
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: katA PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1347 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 452 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 3140 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4640 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 7391 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Melinda J Faulkner, Zhen Ma, Mayuree Fuangthong, John D Helmann
Derepression of the Bacillus subtilis PerR peroxide stress response leads to iron deficiency.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(5);1226-35
[PubMed:22194458]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wang Yung Tu, Susanne Pohl, Pijug Summpunn, Silvio Hering, Sandra Kerstan, Colin R Harwood
Comparative analysis of the responses of related pathogenic and environmental bacteria to oxidative stress.
Microbiology (Reading): 2012, 158(Pt 3);636-647
[PubMed:22174384]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A F Herbig, J D Helmann
Roles of metal ions and hydrogen peroxide in modulating the interaction of the Bacillus subtilis PerR peroxide regulon repressor with operator DNA.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 41(4);849-59
[PubMed:11532148]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Casillas-Martinez, P Setlow
Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, catalase, MrgA, and superoxide dismutase are not involved in resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores to heat or oxidizing agents.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(23);7420-5
[PubMed:9393707]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Engelmann, M Hecker
Impaired oxidative stress resistance of Bacillus subtilis sigB mutants and the role of katA and katE.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1996, 145(1);63-9
[PubMed:8931328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Bsat, L Chen, J D Helmann
Mutation of the Bacillus subtilis alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahpCF) operon reveals compensatory interactions among hydrogen peroxide stress genes.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(22);6579-86
[PubMed:8932315]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Chen, L Keramati, J D Helmann
Coordinate regulation of Bacillus subtilis peroxide stress genes by hydrogen peroxide and metal ions.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1995, 92(18);8190-4
[PubMed:7667267]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)