Difference between revisions of "CodY"
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
** the intracellular concentration of CodY is about 2.5 myM (according to {{PubMed|20408793}}) | ** the intracellular concentration of CodY is about 2.5 myM (according to {{PubMed|20408793}}) | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 955 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 3409 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 17 April 2014
- Description: regulation of a large regulon (more than 100 genes and operons) in response to branched-chain amino acid limitation
| Gene name | codY |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional pleiotropic repressor |
| Function | regulation of a large regulon in response to
branched-chain amino acid limitation to the presence of branched-chain amino acids |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: codY | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CodY | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: codY | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 4.75 |
| Gene length, protein length | 777 bp, 259 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | clpY, flgB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 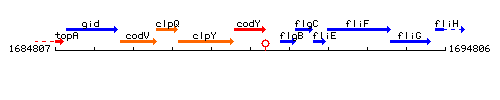
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed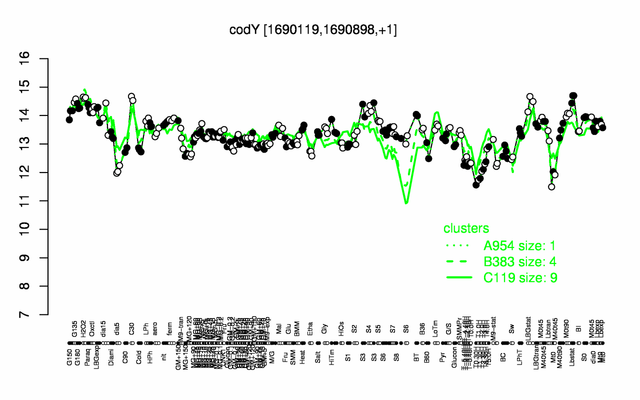
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The CodY regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16170
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
- the mutation suppresses the mucoid phenotype of motA or motB mutants due to loss of DegU phosphorylation and concomitant reduced expression of the capB-capC-capA-capE operon PubMed
- inactivation of codY suppresses the requirement of a relA sasA sasB triple mutant for branched chain amino acids, methionine and threonine PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16170
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: codY family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes/ operons controlled by CodY
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: contains a GAF domain (ligand binding domain)
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-215 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity: GTP and branched chained amino acids (BCAA) increase the affinity of CodY for its DNA target sequences PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16170
- UniProt: P39779
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP566, available in Stülke lab
- a codY::erm mutant is available in Linc Sonenshein's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Tony Wilkinson, York University, U.K. homepage
Oscar Kuipers, University of Groningen, The Netherlands Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Tobias Geiger, Christiane Wolz
Intersection of the stringent response and the CodY regulon in low GC Gram-positive bacteria.
Int J Med Microbiol: 2014, 304(2);150-5
[PubMed:24462007]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sabine Brantl, Andreas Licht
Characterisation of Bacillus subtilis transcriptional regulators involved in metabolic processes.
Curr Protein Pept Sci: 2010, 11(4);274-91
[PubMed:20408793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Abraham L Sonenshein
Control of key metabolic intersections in Bacillus subtilis.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2007, 5(12);917-27
[PubMed:17982469]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Abraham L Sonenshein
CodY, a global regulator of stationary phase and virulence in Gram-positive bacteria.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2005, 8(2);203-7
[PubMed:15802253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
The CodY regulon
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genome-wide identification of Bacillus subtilis CodY-binding sites at single-nucleotide resolution.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2013, 110(17);7026-31
[PubMed:23569278]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of CodY-binding sites in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(4);1224-36
[PubMed:18083814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications
Jia Mun Chan, Sarah B Guttenplan, Daniel B Kearns
Defects in the flagellar motor increase synthesis of poly-γ-glutamate in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(4);740-53
[PubMed:24296669]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Allison Kriel, Shaun R Brinsmade, Jessica L Tse, Ashley K Tehranchi, Alycia N Bittner, Abraham L Sonenshein, Jue D Wang
GTP dysregulation in Bacillus subtilis cells lacking (p)ppGpp results in phenotypic amino acid auxotrophy and failure to adapt to nutrient downshift and regulate biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(1);189-201
[PubMed:24163341]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Baoping Ling, Min Sun, Siwei Bi, Zhihong Jing, Zhiguo Wang
Molecular dynamics simulations of isoleucine-release pathway in GAF domain of N-CodY from Bacillus Subtilis.
J Mol Graph Model: 2013, 44;232-40
[PubMed:23911932]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Allison Kriel, Alycia N Bittner, Sok Ho Kim, Kuanqing Liu, Ashley K Tehranchi, Winnie Y Zou, Samantha Rendon, Rui Chen, Benjamin P Tu, Jue D Wang
Direct regulation of GTP homeostasis by (p)ppGpp: a critical component of viability and stress resistance.
Mol Cell: 2012, 48(2);231-41
[PubMed:22981860]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Andrea Wünsche, Elke Hammer, Maike Bartholomae, Uwe Völker, Andreas Burkovski, Gerald Seidel, Wolfgang Hillen
CcpA forms complexes with CodY and RpoA in Bacillus subtilis.
FEBS J: 2012, 279(12);2201-14
[PubMed:22512862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shaun R Brinsmade, Abraham L Sonenshein
Dissecting complex metabolic integration provides direct genetic evidence for CodY activation by guanine nucleotides.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(20);5637-48
[PubMed:21856856]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lewis V Wray, Susan H Fisher
Bacillus subtilis CodY operators contain overlapping CodY binding sites.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(18);4841-8
[PubMed:21764931]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Roadblock repression of transcription by Bacillus subtilis CodY.
J Mol Biol: 2011, 411(4);729-43
[PubMed:21699902]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Contributions of multiple binding sites and effector-independent binding to CodY-mediated regulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(2);473-84
[PubMed:21097623]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shaun R Brinsmade, Roelco J Kleijn, Uwe Sauer, Abraham L Sonenshein
Regulation of CodY activity through modulation of intracellular branched-chain amino acid pools.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(24);6357-68
[PubMed:20935095]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Anuradha C Villapakkam, Luke D Handke, Boris R Belitsky, Vladimir M Levdikov, Anthony J Wilkinson, Abraham L Sonenshein
Genetic and biochemical analysis of the interaction of Bacillus subtilis CodY with branched-chain amino acids.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(22);6865-76
[PubMed:19749041]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Heike Preis, Rita A Eckart, Rajani K Gudipati, Nadja Heidrich, Sabine Brantl
CodY activates transcription of a small RNA in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(17);5446-57
[PubMed:19542274]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Vladimir M Levdikov, Elena Blagova, Vicki L Colledge, Andrey A Lebedev, David C Williamson, Abraham L Sonenshein, Anthony J Wilkinson
Structural rearrangement accompanying ligand binding in the GAF domain of CodY from Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 390(5);1007-18
[PubMed:19500589]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Daria Julkowska, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Krzysztofa Nagorska, Agnieszka Sekowska, I Barry Holland, Simone J Séror
Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 2);398-412
[PubMed:19202088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Molecular mechanisms underlying the positive stringent response of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon, involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(18);6134-47
[PubMed:18641142]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Luke D Handke, Robert P Shivers, Abraham L Sonenshein
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis CodY with GTP.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(3);798-806
[PubMed:17993518]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wiep Klaas Smits, Tran Thu Hoa, Leendert W Hamoen, Oscar P Kuipers, David Dubnau
Antirepression as a second mechanism of transcriptional activation by a minor groove binding protein.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 64(2);368-81
[PubMed:17493123]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Robert P Shivers, Sean S Dineen, Abraham L Sonenshein
Positive regulation of Bacillus subtilis ackA by CodY and CcpA: establishing a potential hierarchy in carbon flow.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(3);811-22
[PubMed:16995897]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Pascale Joseph, Manoja Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, Abraham L Sonenshein
A region of Bacillus subtilis CodY protein required for interaction with DNA.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(12);4127-39
[PubMed:15937175]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shigeo Tojo, Takenori Satomura, Kaori Morisaki, Josef Deutscher, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Elaborate transcription regulation of the Bacillus subtilis ilv-leu operon involved in the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids through global regulators of CcpA, CodY and TnrA.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 56(6);1560-73
[PubMed:15916606]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Robert P Shivers, Abraham L Sonenshein
Bacillus subtilis ilvB operon: an intersection of global regulons.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 56(6);1549-59
[PubMed:15916605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Robert P Shivers, Abraham L Sonenshein
Activation of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY by direct interaction with branched-chain amino acids.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 53(2);599-611
[PubMed:15228537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hyun-Jin Kim, Sam-In Kim, Manoja Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, Kiyoshi Tachikawa, Abraham L Sonenshein, Mark Strauch
Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(5);1672-80
[PubMed:12591885]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, P Serror, K W Wong, A L Sonenshein
Bacillus subtilis CodY represses early-stationary-phase genes by sensing GTP levels.
Genes Dev: 2001, 15(9);1093-103
[PubMed:11331605]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L V Wray, A E Ferson, S H Fisher
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis ureABC operon is controlled by multiple regulatory factors including CodY, GlnR, TnrA, and Spo0H.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(17);5494-501
[PubMed:9287005]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P Serror, A L Sonenshein
Interaction of CodY, a novel Bacillus subtilis DNA-binding protein, with the dpp promoter region.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 20(4);843-52
[PubMed:8793880]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Slack, P Serror, E Joyce, A L Sonenshein
A gene required for nutritional repression of the Bacillus subtilis dipeptide permease operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 15(4);689-702
[PubMed:7783641]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)