Difference between revisions of "DivIC"
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00620&redirect=T BSU00620] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/yabMNOPQ-divIC-yabR.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/yabMNOPQ-divIC-yabR.html] | ||
| Line 106: | Line 107: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00620&redirect=T BSU00620] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 2 April 2014
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation), component of septosome (with DivIB)
| Gene name | divIC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division protein |
| Function | septum formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: divIC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DivIC | |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 9.968 |
| Gene length, protein length | 375 bp, 125 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yabQ, yabR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 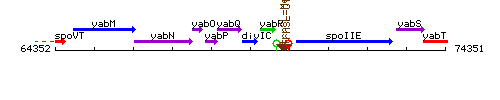
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed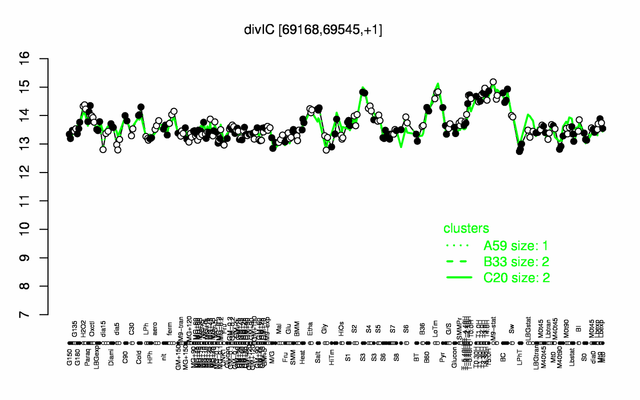
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, sporulation proteins, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigE regulon, SigM regulon, SigW regulon, SigX regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00620
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00620
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane bound PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00620
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37471
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: there are about 50,000 molecules of DivIC per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed