Difference between revisions of "NagR"
| Line 139: | Line 139: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>19342794,20047956 16207374 21602348 23667565</pubmed> | |
| − | <pubmed>19342794,20047956 16207374</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:41, 24 May 2013
- Description: transcriptional regulator (GntR family)
| Gene name | nagR |
| Synonyms | yvoA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator (GntR family) |
| Function | probably regulator of the putative nagA-nagB-yvoA operon |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: nagR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism, Murein recycling | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 6.768 |
| Gene length, protein length | 729 bp, 243 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | nagB, yvnB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 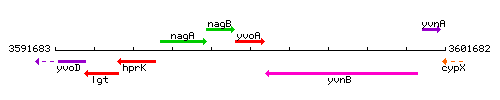
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, transcription factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The NagR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35030
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcription repression of nagP and of the putative nagA-nagB-nagR operon in the absence of N-acetylglycosamine PubMed, weak repression of yflG PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: K(D) for N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate: 1 mM PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: O34817
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Isabelle Gaugué, Jacques Oberto, Harald Putzer, Jacqueline Plumbridge
The use of amino sugars by Bacillus subtilis: presence of a unique operon for the catabolism of glucosamine.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(5);e63025
[PubMed:23667565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Ralph Bertram, Sébastien Rigali, Natalie Wood, Andrzej T Lulko, Oscar P Kuipers, Fritz Titgemeyer
Regulon of the N-acetylglucosamine utilization regulator NagR in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(14);3525-36
[PubMed:21602348]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marcus Resch, Emile Schiltz, Fritz Titgemeyer, Yves A Muller
Insight into the induction mechanism of the GntR/HutC bacterial transcription regulator YvoA.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(7);2485-97
[PubMed:20047956]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marcus Resch, Heide Marie Roth, Mathias Kottmair, Madhumati Sevvana, Ralph Bertram, Fritz Titgemeyer, Yves A Muller
Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of YvoA from Bacillus subtilis.
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun: 2009, 65(Pt 4);410-4
[PubMed:19342794]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
CongHui You, HongYan Lu, Agnieszka Sekowska, Gang Fang, YiPing Wang, Anne-Marie Gilles, Antoine Danchin
The two authentic methionine aminopeptidase genes are differentially expressed in Bacillus subtilis.
BMC Microbiol: 2005, 5;57
[PubMed:16207374]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)