Difference between revisions of "Fur"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=fur_2449841_2450290_-1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:fur_expression.png|500px]] | + | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=fur_2449841_2450290_-1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:fur_expression.png|500px|link=http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU23520]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 16 May 2013
- Description: transcription regulator of iron homoeostasis
| Gene name | fur |
| Synonyms | yqkL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional repressor Fur family |
| Function | regulation of iron homoeostasis
and transcription of ferri-siderophore uptake genes |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: fur
and transcription of ferri-siderophore uptake genes | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Metal ion homeostasis, Alternative nitrogen sources, Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 5.374 |
| Gene length, protein length | 447 bp, 149 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqzK, spoIIM |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 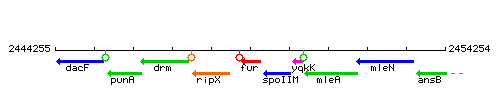
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed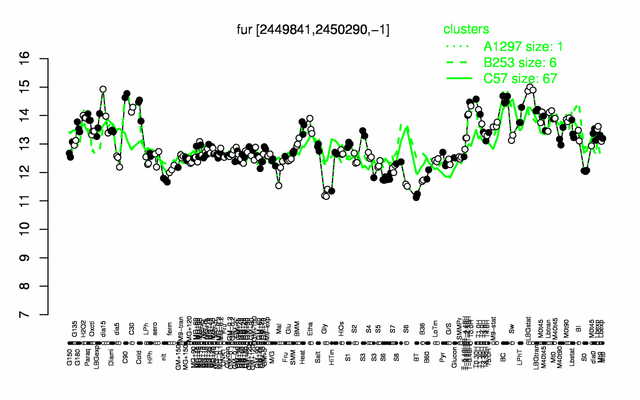
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
iron metabolism, transcription factors and their control
- see also: glutamate metabolism
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The Fur regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23520
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no growth with glucose and ammonium as single sources of carbon and nitrogen, respectively (due to FsrA-mediated repression of the gltA-gltB operon) PubMed
- poor frowth on lactate as single carbon source (due to overexpression of FsrA-mediated repression of the lutA-lutB-lutC operon, can be suppressed by inactivation of fsrA or fbpB) PubMed
- transcription profile of a fur mutant strain: GEO PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Fur family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): contains an iron-sulfur cluster
- Effectors of protein activity:
- DNA binding activity (repression) is triggered by binding of Fe(II) PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54574
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: fur PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: HB6543 (aphA3), available in the John Helmann lab; also available in the Stülke lab GP879 (fur::mls) and GP868 (fur::mls, perR::spc)
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
John Helmann, Cornell University, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
The Fur regulon
Addititonal publications: PubMed
Other original publications
Addititonal publications: PubMed