Difference between revisions of "Rnc"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>9393702 11123676 7527387 9677377 17576666, 11021934 6409421 22123973 22412379 23300471 </pubmed> | + | |
| + | <pubmed>9393702 11123676 7527387 9677377 17576666, 11021934 6409421 22123973 22412379 23300471</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 10 January 2013
- Description: RNase III; required for the degradation of sense/antisense transcripts in Gram positive, low GC bacteria
| Gene name | rnc |
| Synonyms | rncS |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | endoribonuclease III |
| Function | cleaves both 5'- and 3'-sites of the small cytoplasmic RNA precursor (scr) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rnc | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 8.076 |
| Gene length, protein length | 747 bp, 249 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | acpA, smc |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed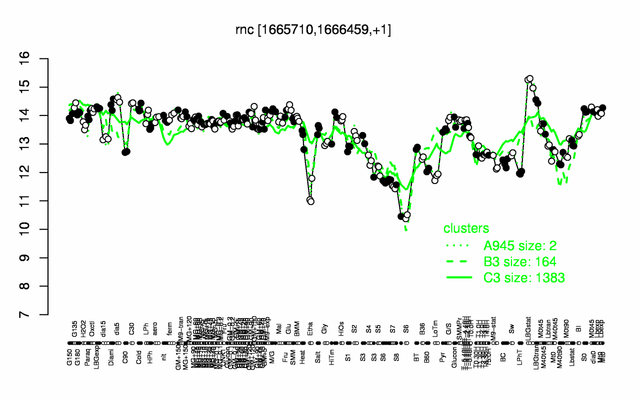
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
Rnases, translation, protein secretion, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15930
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- the rnc gene can be deleted in strains cured of the Skin element and prophage SPß (or upon deletion of the toxin genes txpA and yonT) PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Endonucleolytic cleavage of double-stranded RNA to 5'-phosphomonoester (according to Swiss-Prot)
- cleaves both 5'- and 3'-sites of the small cytoplasmic RNA precursor (scr)
- degradation of txpA mRNA-RatA RNA duplex (encoded on the Skin element) PubMed
- degradation of yonT mRNA-as-YonT RNA duplex (encoded on the SP-beta prophage) PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P51833
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.1.26.3
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
David Bechhofer, Mount Sinai School, New York, USA Homepage
Ciaran Condon, IBPC, Paris, France Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Fabian M Commichau, Jörg Stülke
A mystery unraveled: essentiality of RNase III in Bacillus subtilis is caused by resident prophages.
PLoS Genet: 2012, 8(12);e1003199
[PubMed:23300472]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ian J MacRae, Jennifer A Doudna
Ribonuclease revisited: structural insights into ribonuclease III family enzymes.
Curr Opin Struct Biol: 2007, 17(1);138-45
[PubMed:17194582]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Xinhua Ji
Structural basis for non-catalytic and catalytic activities of ribonuclease III.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr: 2006, 62(Pt 8);933-40
[PubMed:16855311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Djamel Drider, Ciarán Condon
The continuing story of endoribonuclease III.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2004, 8(4);195-200
[PubMed:16179796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R A Srivastava, N Srivastava
The multifaceted roles of the RNA processing enzyme ribonuclease III.
Indian J Biochem Biophys: 1996, 33(4);253-60
[PubMed:8936814]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
Original publications