Difference between revisions of "DynA"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell division]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell shape]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane dynamics]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane dynamics]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | ||
| Line 94: | Line 96: | ||
** associated to the membrane {{PubMed|21205012}} | ** associated to the membrane {{PubMed|21205012}} | ||
** membrane, forms foci at the site of septation {{PubMed|23060960}} | ** membrane, forms foci at the site of septation {{PubMed|23060960}} | ||
| + | ** colocalizes with [[FtsZ]] {{PubMed|23249255}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 143: | Line 146: | ||
<pubmed> 23109540 20970992 21599493 15040446 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 23109540 20970992 21599493 15040446 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed> 8396117 21205012 20525796 23060960</pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 8396117 21205012 20525796 23060960 23249255 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:58, 20 December 2012
- Description: dynamin-like protein, mediates membrane fusion
| Gene name | dynA |
| Synonyms | ypbR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | dynamin-like protein |
| Function | fusion of membranes |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: dynA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DynA | |
| MW, pI | 137 kDa, 5.724 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3579 bp, 1193 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ypbS, fbpC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 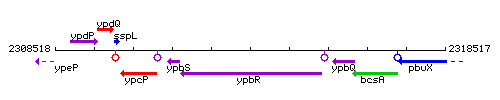
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, cell shape, membrane dynamics, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22030
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: mediates nucleotide independent membrane fusion in vitro PubMed
- Protein family: gerABKA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two separate dynamin-like subunits and GTPase domains PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): Mg(2+) PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54159
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: dynA PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications