|
|
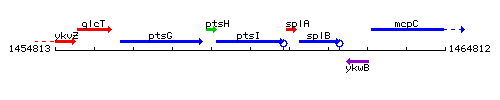
| Line 124: |
Line 124: |
| | =References= | | =References= |
| | | | |
| − | # Pompeo F, Luciano J, Galinier A. (2007) Interaction of GapA with HPr and its homologue, Crh: Novel levels of regulation of a key step of glycolysis in Bacillus subtilis? ''J Bacteriol.'' '''189(3):''' 1154-7. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17142398 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Arnaud M, Vary P, Zagorec M, Klier A, Débarbouillé M, Postma P, Rapoport G (1992) Regulation of the sacPA operon of Bacillus subtilis: identification of phosphotransferase system components involved in SacT activity. J Bacteriol 174:3161-3170. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/1577686 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Deutscher, J., Kessler, U., Alpert, C. A., and Hengstenberg, W. (1984) Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: P-ser-HPr and its possible regulatory function. Biochemistry 23: 4455-4460. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi00314a033 DOI:10.1021/bi00314a033]
| |
| − | # Deutscher, J., Küster, E., Bergstedt, U., Charrier, V., and Hillen, W. (1995) Protein kinase-dependent HPr/CcpA interaction links glycolytic activity to carbon catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 15: 1049-1053. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7623661 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Eisermann, R., Deutscher, J., Gonzy-Tréboul, G., and Hengstenberg, W. (1988) Site-directed mutagenesis with the ptsH gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 263: 17050-17054. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2846556 PubMed]
| |
| | # Frisby, D., and Zuber, P. 1994. Mutations in pts cause catabolite-resistant sporulation and altered regulation of spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 176: 2587-2595. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8169206 PubMed] | | # Frisby, D., and Zuber, P. 1994. Mutations in pts cause catabolite-resistant sporulation and altered regulation of spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 176: 2587-2595. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8169206 PubMed] |
| − | # Galinier A, Deutscher J, Martin-Verstraete I: (1999) Phosphorylation of either Crh or HPr mediates binding of CcpA to the Bacillus subtilis xyn cre and catabolite repression of the xyn operon. J Mol Biol , 286:307-314. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9973552 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Görke, B., Fraysse, L. & Galinier, A. (2004) Drastic differences in Crh and HPr synthesis levels reflect their different impacts on catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2992-2995 . [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15126459 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Lindner, C., Galinier, A., Hecker, M. & Deutscher, J. (1999) Regulation of the activity of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator LicT by multiple PEP-dependent, enzyme I- and HPr-catalysed phosphorylation. Mol. Microbiol. 31, 995-1006 . [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10048041 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Lindner, C., Hecker, M., Le Coq, D. & Deutscher, J. (2002) Bacillus subtilis mutant LicT antiterminators exhibiting enzyme I- and HPr-independent antitermination affect catabolite repression of the bglPH operon. J. Bacteriol. 184, 4819-4828 . [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12169607 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Martin-Verstraete, I., Charrier, V., Stülke, J., Galinier, A., Erni, B., Rapoport, G., & Deutscher, J. (1998) Antagonistic effects of dual PTS catalyzed phosphorylation on the Bacillus subtilis transcriptional activator LevR. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 293-303. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9622354 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Martin-Verstraete, I., Deutscher, J., and Galinier, A. (1999) Phosphorylation of HPr and Crh by HprK, early steps in the catabolite repression signalling pathway for the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J Bacteriol 181: 2966-2969. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10217795 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Reizer, J., Sutrina, S. L., Saier, Jr., M. H., Stewart, G. C., Peterkofsky, A., and Reddy, P. (1989) Mechanistic and physiological consequences of HPr(Ser) phosphorylation on the activities of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Gram-positive bacteria: studies with site-specific mutants of HPr. EMBO J 8: 2111-2120. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2507315 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Schmalisch, M., Bachem, S. & Stülke, J. (2003) Control of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator protein GlcT by phosphorylation: Elucidation of the phosphorylation chain leading to inactivation of GlcT. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 51108-51115. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/14527945 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Schumacher, M. A. et al. (2004) Structural basis for allosteric control of the transcription regulator CcpA by the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P. Cell 118, 731-741 . [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15369672 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Singh, K. D., Halbedel, S., Görke, B. & Stülke, J. (2007) Control of the phosphorylation state of the HPr protein of the phosphotransferase system in Bacillus subtilis: implication of the protein phosphatase PrpC. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13: 165-171. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17693724 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Singh, K. D., Schmalisch, M. H., Stülke, J. & Görke, B. (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: A quantitative analysis of repression exerted by different carbon sources. J. Bacteriol. 190: 7275-7284. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18757537 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Stülke, J., Martin-Verstraete, I., Charrier, V., Klier, A., Deutscher, J. & Rapoport, G. (1995) The HPr protein of the phosphotransferase system links induction and catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6928-6936. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7592487 PubMed]
| |
| − | # Tortosa, P., Aymerich, S., Lindner, C., Saier, M.H., Jr., Reizer, J. and Le Coq, D. (1997) Multiple phosphorylation of SacY, a Bacillus subtilis antiterminator negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17230-17237. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9202047 PubMed]
| |