Difference between revisions of "ZapA"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of Z-ring formation | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of Z-ring formation | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtiexpress/bsu/BSU28610 zapA] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/ZapA ZapA] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/ZapA ZapA] | ||
Revision as of 14:41, 7 August 2012
- Description: positive modulator of FtsZ Z ring assembly and stability
| Gene name | zapA |
| Synonyms | yshA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | Z-ring-associated protein |
| Function | control of Z-ring formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: zapA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ZapA | |
| MW, pI | 9 kDa, 7.17 |
| Gene length, protein length | 255 bp, 85 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yshB, rnhC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 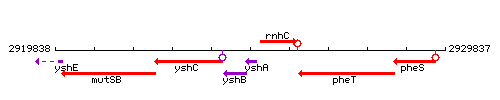
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Type 2 subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P94542
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications